This comprehensive guide introduces the 10 most essential Excel function that can dramatically improve your spreadsheet skills. Covering both basic and advanced excel functions, from basic calculations to complex data analysis, mastering these functions will enhance your efficiency and productivity in Excel.
by Mihir Kamdar / Last Updated:
In this guide, you’ll discover essential Excel functions that will enhance your data management skills and streamline your workflow, including:
How to perform quick calculations with SUM
Creating conditional logic using IF statements
Efficient data retrieval techniques with VLOOKUP and XLOOKUP
Advanced lookup strategies using INDEX-MATCH
Counting and analyzing data with COUNT, COUNTA, SUMIF, and COUNTIF
Combining text strings with TEXTJOIN
Filtering and extracting unique data with FILTER and UNIQUE
Download our step-by-step tutorial file now by clicking on the icon below and follow along to enhance your Excel skills practically and efficiently!
Microsoft Excel is a data management and analysis powerhouse, but its true potential is unlocked when you master its key functions. Understanding these essential Excel functions can dramatically improve your efficiency and productivity, whether you’re a business professional, student, or data enthusiast. This article will guide you through the top 10 Excel functions that every user should know.
By mastering each function in excel, you’ll be able to streamline your workflow, perform complex calculations with ease, and extract valuable insights from your data. Let’s dive into the world of Excel functions and discover how they can transform your spreadsheet skills.
Excel functions are predefined formulas designed to perform specific calculations or data manipulations. They allow users to automate repetitive tasks and streamline complex operations like summing values, counting cells, and retrieving data. Functions can handle mathematical, logical, text, or lookup operations.
Excel’s functions simplify data analysis by ensuring accuracy and efficiency. Each function follows a defined syntax, and understanding how to use these functions can greatly enhance your productivity in Excel. Examples include SUM, IF, VLOOKUP, and COUNTIF, among many others.
Excel functions are predefined formulas that perform calculations using specific values in a particular order. These functions are essential tools for anyone looking to maximize their productivity in Excel. By understanding how to use functions, you can quickly find the sum, average, count, maximum value, and minimum value for a range of cells, among other calculations.
Each function in Excel has a specific syntax, which includes the function name followed by arguments enclosed in parentheses. The arguments can be numbers, text values, cell references, or other functions. For example, the SUM function adds a range of numbers, while the AVERAGE function calculates the mean of a range of values. Understanding how to create and use these arguments is crucial for performing accurate calculations.
Functions can be used for a variety of tasks, including mathematical operations, text manipulation, and logical tests. By mastering these functions, you can streamline your workflow and perform complex calculations with ease, making Excel an even more powerful tool for data analysis and management.
Excel functions are predefined formulas designed to perform specific calculations and data manipulations efficiently. These functions are the backbone of Excel’s powerful data analysis capabilities, allowing users to quickly find the sum, average, count, maximum value, and minimum value for a range of cells.
Whether you’re dealing with financial data, statistical analysis, or engineering calculations, Excel functions can simplify complex tasks and enhance your productivity.
Each function in Excel follows a specific syntax, typically consisting of the function name followed by arguments enclosed in parentheses. These arguments can be numbers, text values, cell references, or even other functions.
For instance, the SUM function adds a range of numbers, while the AVERAGE function calculates the mean of a range of values. By mastering these functions, you can perform accurate calculations and streamline your workflow, making Excel an indispensable tool for data management and analysis.
To fix Excel errors, start by identifying common formula errors such as incorrect references or missing arguments. Excel’s error checking feature helps highlight issues like numeric values used incorrectly in formulas.
Enable background error checking ensures that Excel flags potential excel error while you work. Once identified, you can adjust the formula to match the desired function or correct the formula syntax. Excel also provides function counts errors and display messages when a function count exceeds expectations, helping maintain data accuracy.
Excel commands are essential for streamlining tasks, making them an indispensable part of data analysis. With tools like analysis for excel, users can easily interpret and visualize data, while a list of excel functions can help users quickly access the full potential of the software. For advanced users, advanced excel commands and advanced excel formulas in excel open up even more possibilities for complex data manipulation.
Some of the most useful excel functions include those that enhance calculation efficiency, while using formulas in excel is central to automating repetitive tasks. The best excel functions simplify data processing, and common excel functions are indispensable for everyday tasks. The excel function and allows users to combine multiple logical operations, while statistical functions in excel are valuable for data analysis.
Other useful excel formulas can further enhance productivity and help with specialized tasks. In any Excel workspace, mastering the most important excel functions and the popular excel functions can significantly boost efficiency, making Excel an even more powerful tool for both beginners and advanced users.
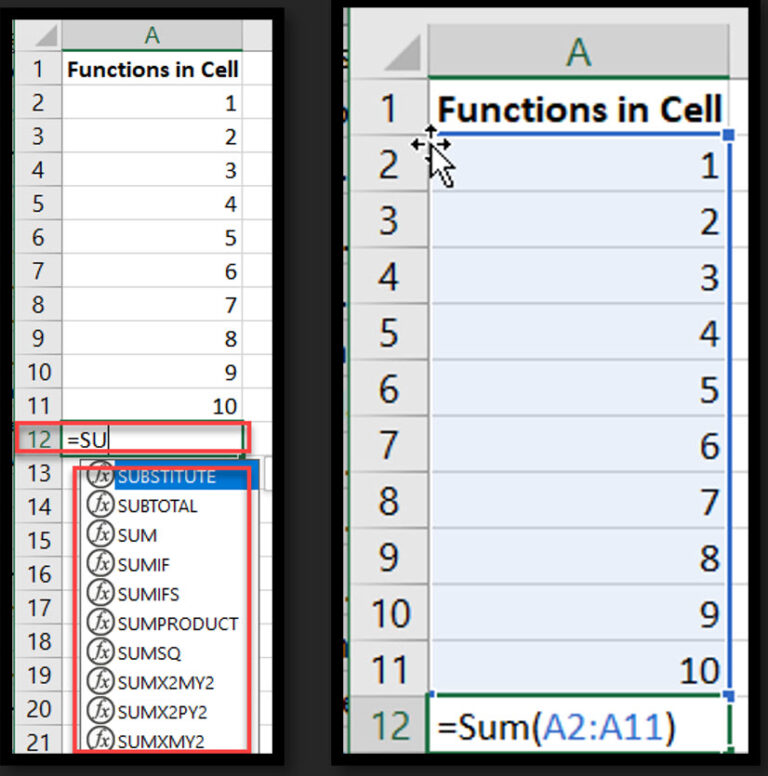
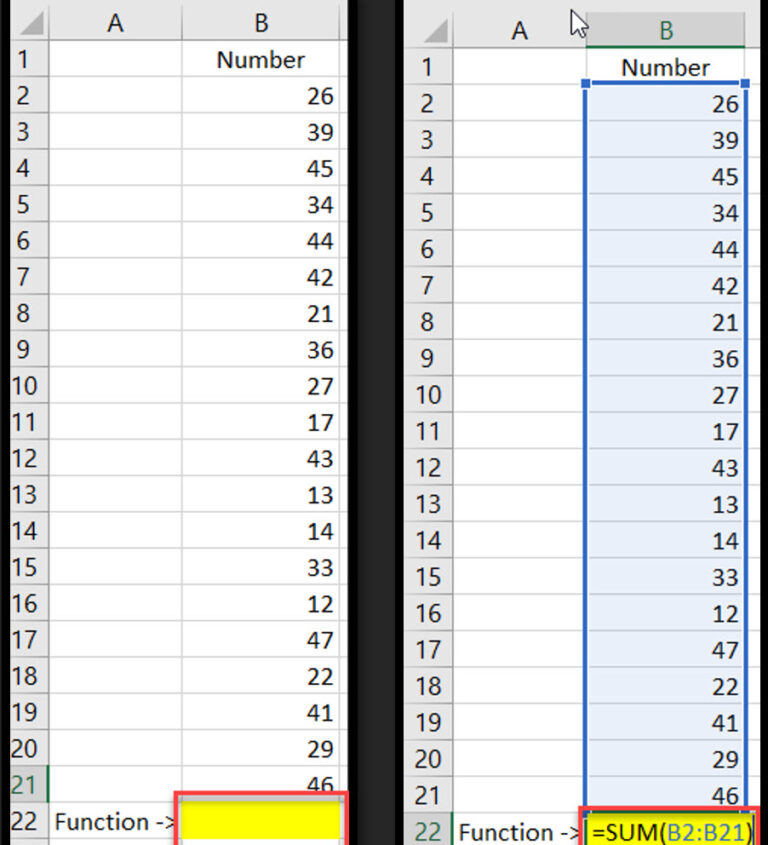
The SUM function adds a range of numbers and returns the total.
Syntax: =SUM(number1, [number2], …)
Example: =SUM(B2:B21) adds all values in cells B2 through B21 using cell references.
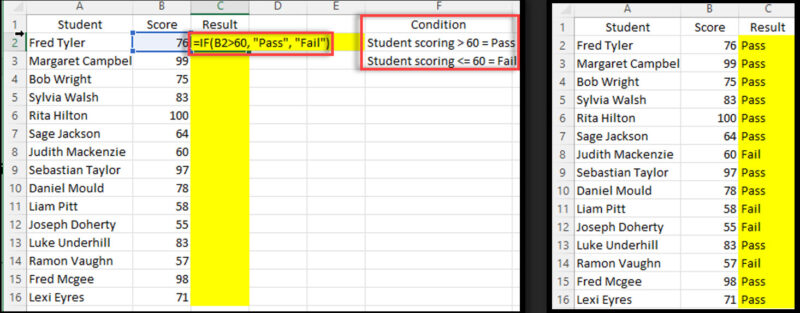
The IF function performs a logical test and returns one value if the test is true and another if it’s false, based on logical values like TRUE or FALSE.
Syntax: =IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false)
Example: =IF(B2>60, “Pass”, “Fail”)
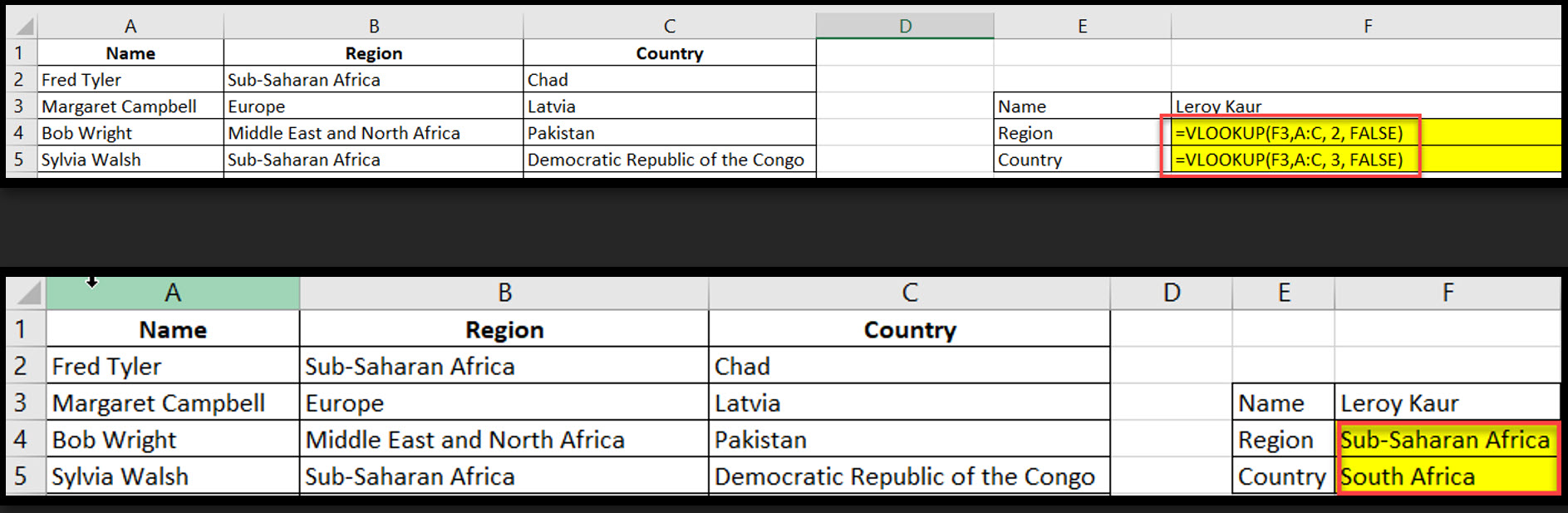
VLOOKUP searches for a value in the first column of a table and returns a corresponding value from a specified column in the same row.
Syntax: =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
Example: =VLOOKUP(F3,A:C, 2, FALSE)
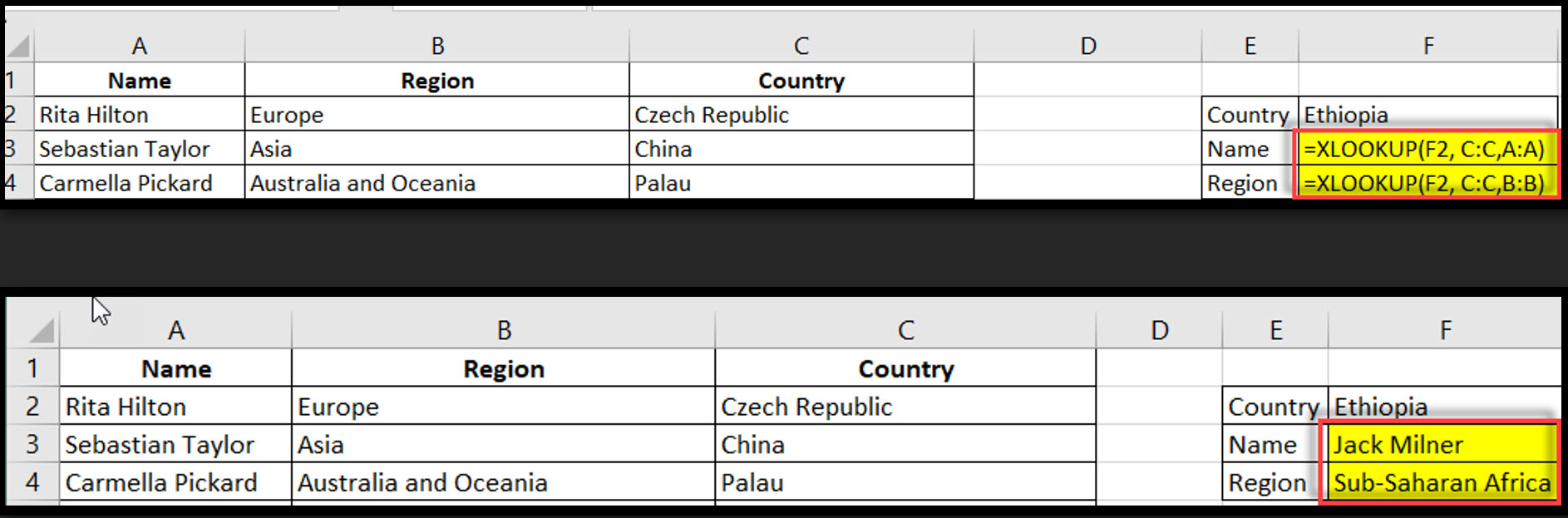
XLOOKUP is a more versatile alternative to VLOOKUP, allowing lookups in any direction and returning multiple values.
Syntax: =XLOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_array, return_array, [if_not_found], [match_mode], [search_mode])
Example: =XLOOKUP(F2, C:C,A:A, “Not Found”)
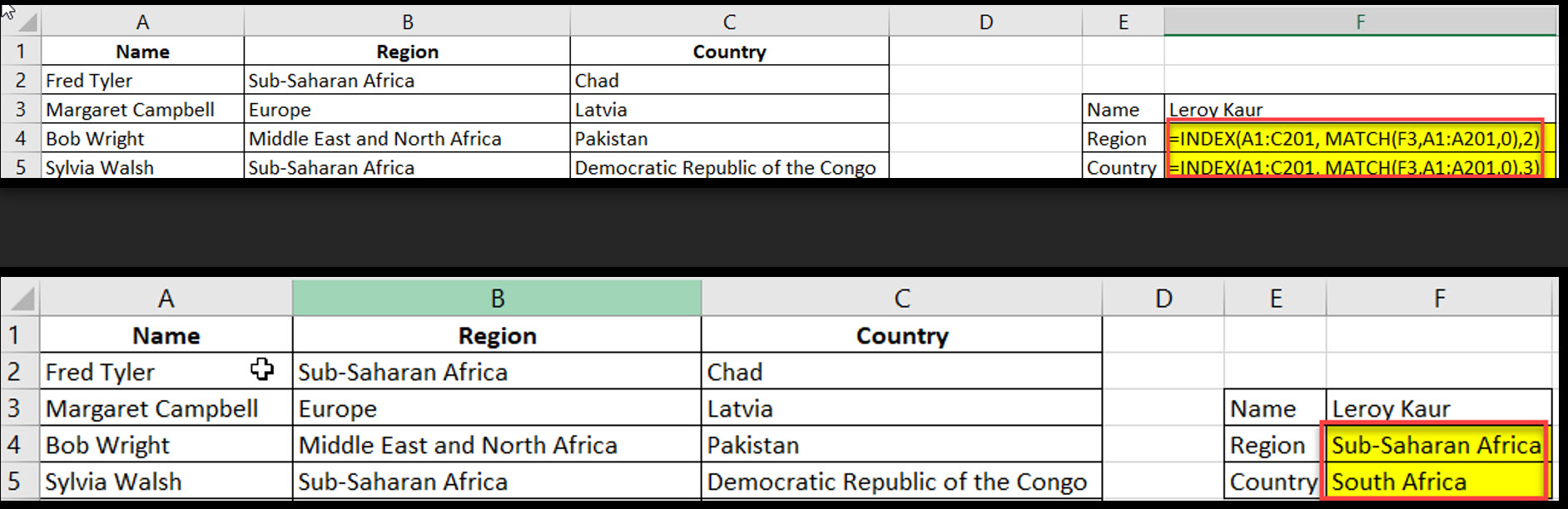
INDEX-MATCH is a powerful combination of two functions that allows for flexible, two-way lookups.
Syntax: =INDEX(return_range, MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_range, 0))
Example: =INDEX(A1:C201, MATCH(F3,A1:A201,0),2).
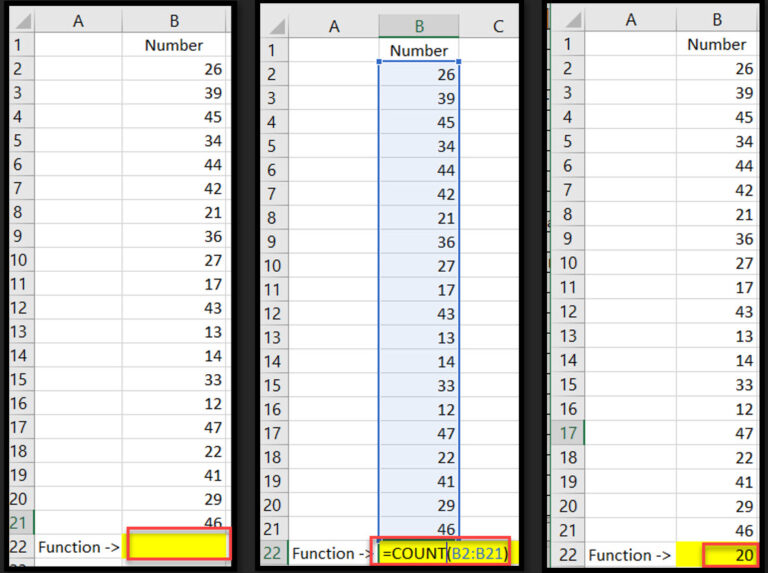
COUNT tallies cells containing numbers, while COUNTA counts non-empty cells, including text values.
Syntax:
=COUNT(value1, [value2], …)
=COUNTA(value1, [value2], …)
Example: =COUNT(B2:B21)
TEXTJOIN combines text from multiple ranges and/or strings, and includes a delimiter you specify between each text value that will be combined.
Syntax: =TEXTJOIN(delimiter, ignore_empty, text1, [text2], …)
Example: TEXTJOIN(” “,True, B2, C2). joins the text in B2:C2, separated by commas, ignoring empty cells.

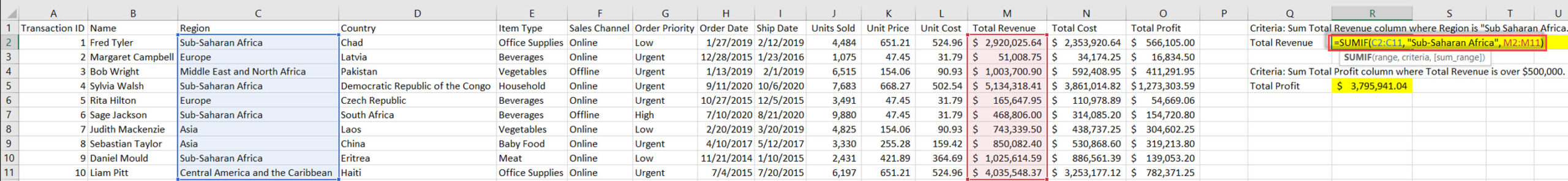
SUMIF adds cells that meet a specific criterion.
Syntax:
=SUMIF(range, criteria, [sum_range])
Example: =SUMIF(C2:C11, “Sub-Saharan Africa”, M2:M11)
FILTER returns a filtered range based on specified criteria.
Syntax: =FILTER(array, include, [if_empty])
Example: =FILTER(A2:C201, B2:B201 = G3)

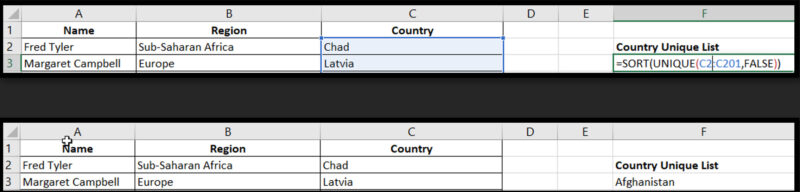
UNIQUE returns a list of unique values from a range of cells.
Syntax: =UNIQUE(array, [by_col], [exactly_once])
Example: =SORT(UNIQUE(C2:C201,FALSE))
The SUM function in Excel is used to add a range of numbers quickly. You can use it to calculate totals from rows or columns of data, saving time in manual addition.
Excel formulas, like SUM, IF, and VLOOKUP, automate calculations and enhance your data analysis by processing values automatically based on specific conditions.
Common Excel errors can occur due to incorrect syntax, invalid cell references, or mismatched data types. Always ensure that your formulas have the correct cell references and argument types.
Cell references determine the input values for Excel formulas. Correctly referencing cells ensures accurate calculations and allows for dynamic updates when data changes
Mastering these 10 essential Excel functions will significantly enhance your ability to manage, analyze, and derive insights from your data. From basic calculations with SUM to complex data retrieval with INDEX-MATCH and data filtering with FILTER, these functions form the foundation of efficient Excel use.
As you become more comfortable with these functions, you’ll find your productivity soaring and your ability to handle complex data tasks greatly improved. Remember, the key to mastering Excel is practice. Try incorporating these functions into your daily Excel tasks, and don’t be afraid to explore more advanced features as your confidence grows.
Excel formulas play a pivotal role in enhancing productivity and data management. Popular formulas like excel or function and excel and function simplify logical operations, making complex data analysis more intuitive. The diverse range of excel function options and the comprehensive excel functionality allow users to handle tasks efficiently. Leveraging excel tips and tricks can further optimize workflows. Analysts frequently ask, whih excel formulas do financial analysts use in excel, highlighting the importance of targeted formulas in financial contexts. Accessing an excel formulas list or mastering functions in excel empowers users to streamline processes and make informed decisions, showcasing the software’s versatility.

92% of students automate workflows, build CEO-ready dashboards, and streamline collaboration in < 1 hour. Don’t miss out!
🎯Master every Office 365 tool like Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Teams, Outlook and OneNote.
🎯Streamlined approach—no fluff, just rapid skill-building.
🎯Eliminate tedious tasks with intelligent automation.
🎯Transform everyday workflows into strategic power moves.
🎯Boost productivity and impress every boss.
🎯Real-World Projects – directly translate lessons into workplace wins.