This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Excel Errors and Formula Auditing, providing essential knowledge for troubleshooting and optimizing spreadsheets.
by Mihir Kamdar / Last Updated:
In this guide, you’ll learn how to troubleshoot Excel formulas and fix errors effectively, including:
Fix 9 common Excel formula errors with practical solutions
Master 7 Formula Auditing tools
How to visualise formula relationships and dependencies
Step by step process to evaluate and debug complex formulas
Download our step-by-step tutorial file now by clicking on the icon below and follow along to enhance your Excel skills practically and efficiently!
Microsoft Excel is a data analysis and management beast but as spreadsheets get more complex so do the formula errors. Excel’s Formula Auditing tools are designed to help you understand, troubleshoot, and optimize your formulas, so you can get accurate and efficient results while minimizing errors in Excel. This guide will go through the most common formula errors and explain in detail the tools to fix them.
Excel errors can be frustrating and time-consuming to troubleshoot. Understanding the different types of Excel errors can help you avoid them and fix them quickly. Excel errors are usually presented with strange letters and numerals or exclamation marks containing little information about what is happening in the formula.
Formulas in Excel play a crucial role in data analysis, but users often encounter challenges such as formulas not working in Excel or dealing with value errors in Excel. Common issues include Excel showing formulas instead of calculated results, which can be resolved by adjusting cell formatting or toggling off the formula view. Errors formula issues, like incorrect syntax or invalid references, are frequent hurdles, and learning how to fix error Excel can save significant time. Built-in tools like the Error Checking feature are valuable for resolving errors formula problems.
Understanding how to remove formula in Excel is essential for simplifying spreadsheets while keeping calculated values intact. Many users search for solutions on how to remove a formula in Excel to make their data presentation cleaner. Troubleshooting Excel error scenarios, such as #VALUE! or #REF!, can be streamlined with functions like IFERROR and auditing techniques. The and or formula is especially helpful for creating conditional logic to solve complex data problems effectively. By mastering these solutions, users can avoid frustration and ensure smooth data management in Excel.
To fix formula errors in Excel, you can use the Evaluate Formula tool under the Formulas tab. This tool lets you step through a formula, helping you identify errors step by step. Additionally, the Error Checking dialog box provides a comprehensive error report and potential solutions. For a quick view of formulas, the Formula Bar displays the active formula, allowing easy editing and troubleshooting of cell references and other formula components.
In Excel, the Formula Auditing group under the Formulas tab helps manage and debug errors. When a circular reference occurs, it means a formula refers to its own cell, creating an endless loop. This can cause incorrect calculations. Additionally, Excel functions like date calculations may result in a negative date value if the date is earlier than the Excel start date (January 1, 1900). These issues can be resolved using tools within an Excel worksheet to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Managing errors and formulas in Excel can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can streamline your work. If you’re wondering how to show error message in spreadsheet, functions like IFERROR can be used to display custom messages for invalid data. For complex workbooks, it’s crucial to know how to check calculation error efficiently. Excel’s Formula Auditing tools allow users to trace dependencies and identify issues like incorrect references.
When dealing with excel errors like “Excel found a problem with formula references,” ensure your ranges and dependencies are accurate. If your spreadsheet needs to know which cell has error, Excel highlights such cells automatically, or you can use Error Checking in the Formula tab. If you want to know how to get rid of formulas in Excel, you can replace formulas with their calculated values by copying and pasting them as values. Alternatively, learning how to remove formula in Excel is helpful when preparing spreadsheets for sharing.
For users struggling with Excel showing formula instead of results, check for text-formatted cells or missing = signs. When exploring how to do the formula in Excel, remember that $ in Excel formula locks references, aiding in creating adaptable calculations. These tips will help you manage formulas and errors efficiently, saving time and effort.
Excel formula errors like #NAME?, #DIV/0!, or #REF! indicate issues with syntax, data types, or cell references in spreadsheets. Understanding these errors and their solutions is crucial for maintaining accurate calculations and efficient data management in Excel.
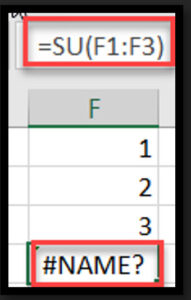
Cause: Excel doesn’t recognize a function name used in a formula, often due to typos, incorrect range name formatting, or missing quotes.
Example: Using “SU” instead of “SUM” in a formula.
Solution:
Check for typos in function names
Ensure range names are properly formatted
Use the Insert Function dialog box (Formulas > Insert Function) to avoid syntax errors
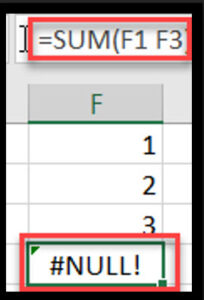
Cause: Incorrect use of range operator (space) instead of range operator (:).
Example: =SUM(A1 A3) instead of =SUM(A1:A3)
Solution:
Check for colons (:) in range references
Review formula syntax when combining ranges
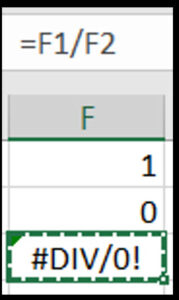
Cause: Occurs when a formula tries to divide by zero or an empty cell, resulting in an Excel error.
Solution:
Enter valid numbers in cells used for division
Use error handling functions like IFERROR or IF to manage divide by zero scenarios
Use the AVERAGE function to calculate the mean of a range of cells, which can help avoid division by zero errors
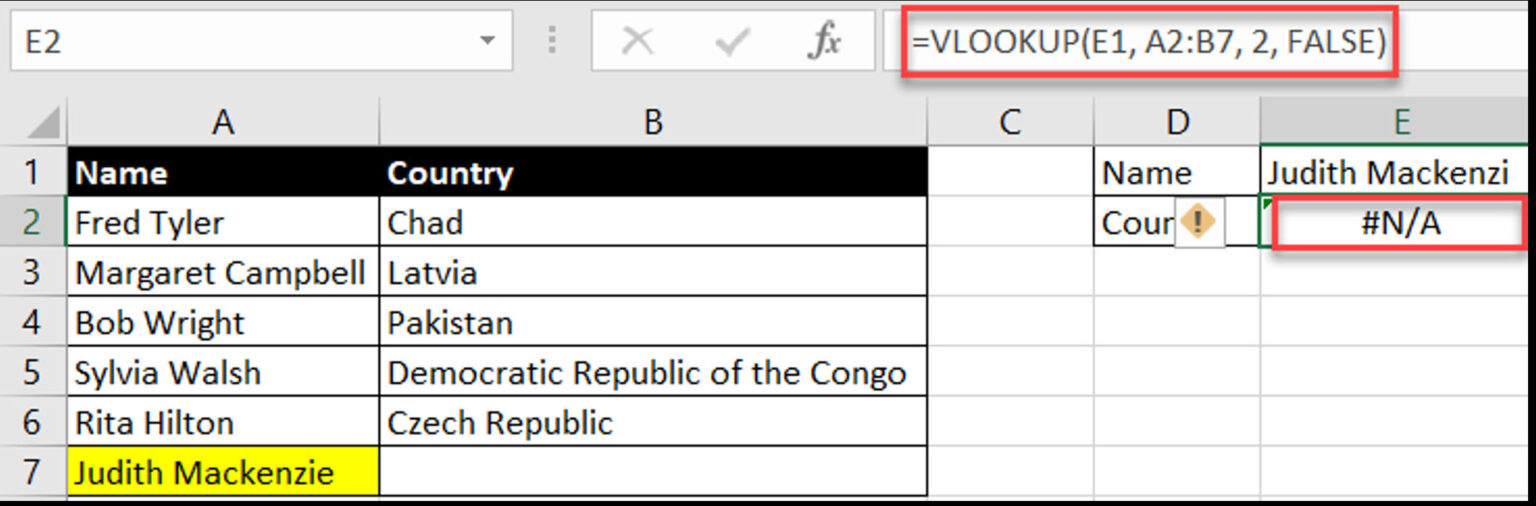
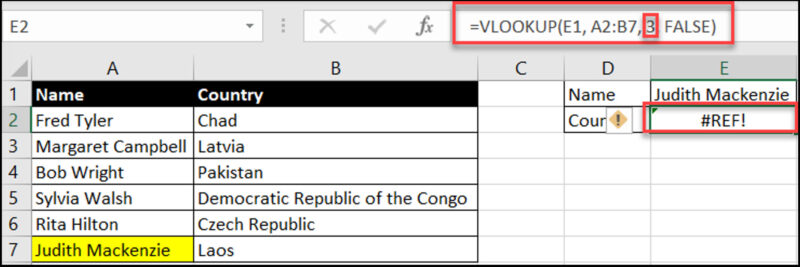
Cause: Appears when a lookup function (e.g. VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, INDEX & MATCH) can’t find the value.
Example: Misspelling “Judith Mackenzie” as “Judith Mackenzi” in a VLOOKUP function can result in the lookup value not being found.
Solution:
Use the IFNA function to return alternative results when a value is not found
Double check spelling and data consistency in lookup values
Ensure lookup ranges are correctly defined
Cause: Invalid cell reference, often due to deleted cells or incorrect column/row references.
Solution:
Check all cell references in formulas
Adjust formulas if cells or ranges have been moved or deleted
Use named ranges to make formulas more robust to structural changes
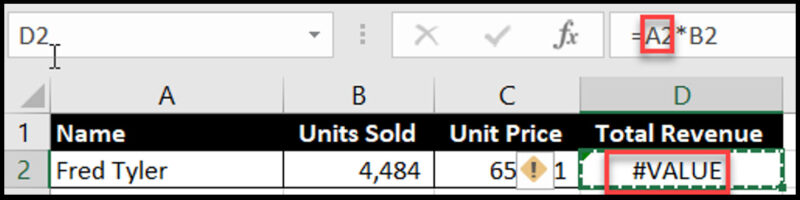
Cause: Using the wrong data type in a formula or function.
Example: Trying to do a math operation on text data.
Solution:
Ensure cells referenced in formulas contain the correct data type
Use the VALUE() function to convert text to numbers when needed
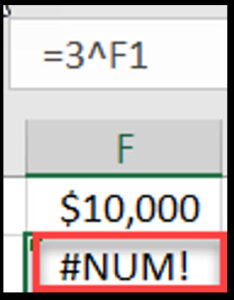
Cause: Occurs when a formula returns a number too large or too small for Excel to handle or when using invalid numbers in mathematical functions, requiring you to fix Excel errors.
Solution:
Check for extremely large or small numbers in calculations
Verify mathematical functions are using valid inputs
Break down complex calculations into smaller steps
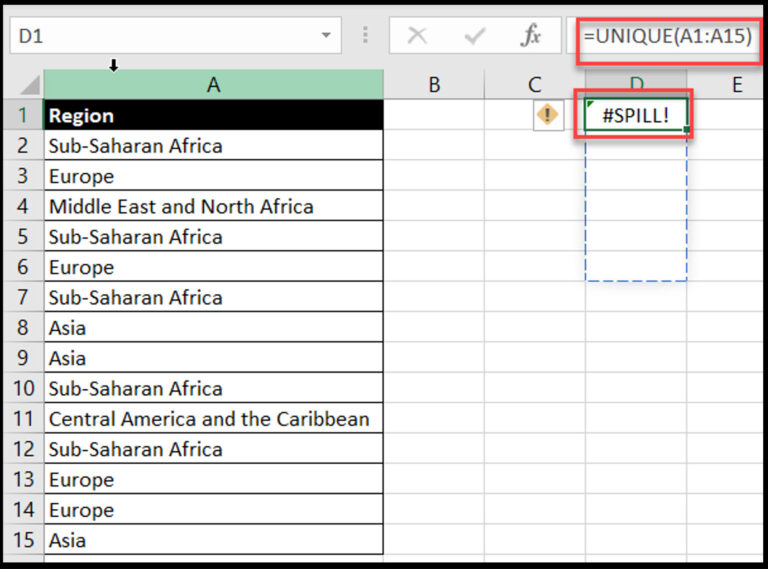
Cause: Happens when a dynamic array formula’s output range is blocked by existing data.
Solution:
Clear cells blocking the spill range
Ensure there are enough empty cells for the formula to spill into
Rearrange your worksheet layout to accommodate dynamic arrays
Monitor and manage outputs to multiple cells to avoid the #SPILL! error by ensuring no existing data obstructs the output range
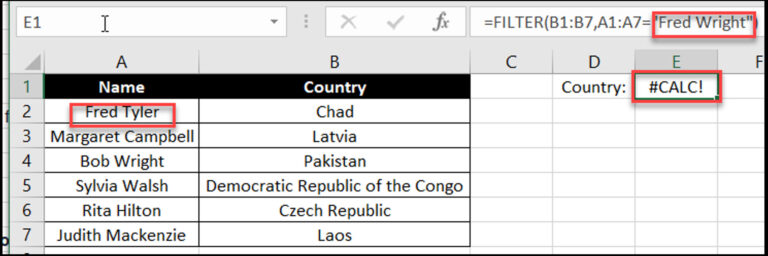
Cause: Typically occurs when the FILTER function can’t return a result, often because no matches were found.
Solution:
Include a “Not Found” argument in the FILTER function
Check the filter criteria
Verify the data being filtered has the expected value
Excel’s Formula Auditing Tools provide powerful features for visualizing, understanding, and troubleshooting complex formulas. These tools, including Trace Precedents, Trace Dependents, and Evaluate Formula, help users identify error sources and optimize their spreadsheets for improved accuracy and performance.
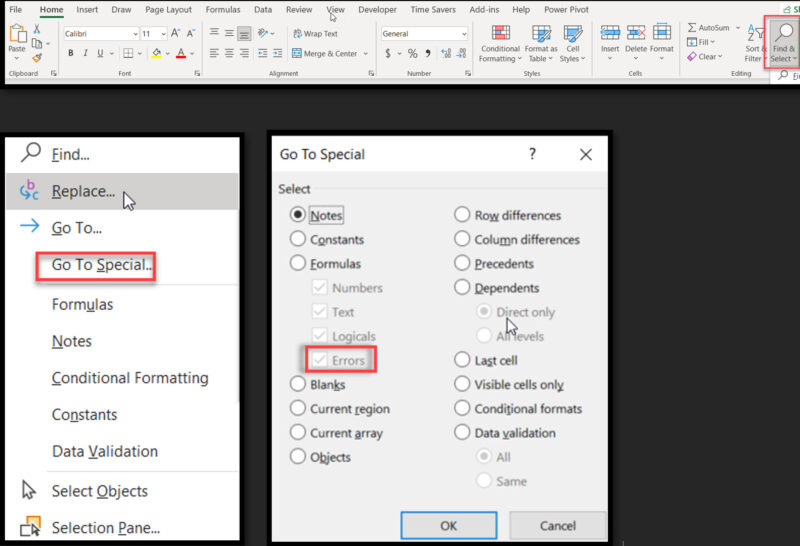
Purpose: Find cells with specific properties, including errors or formulas.
How to:
Go to Home > Find & Select > Go To Special
Select “Formulas” and “Errors”
Click OK
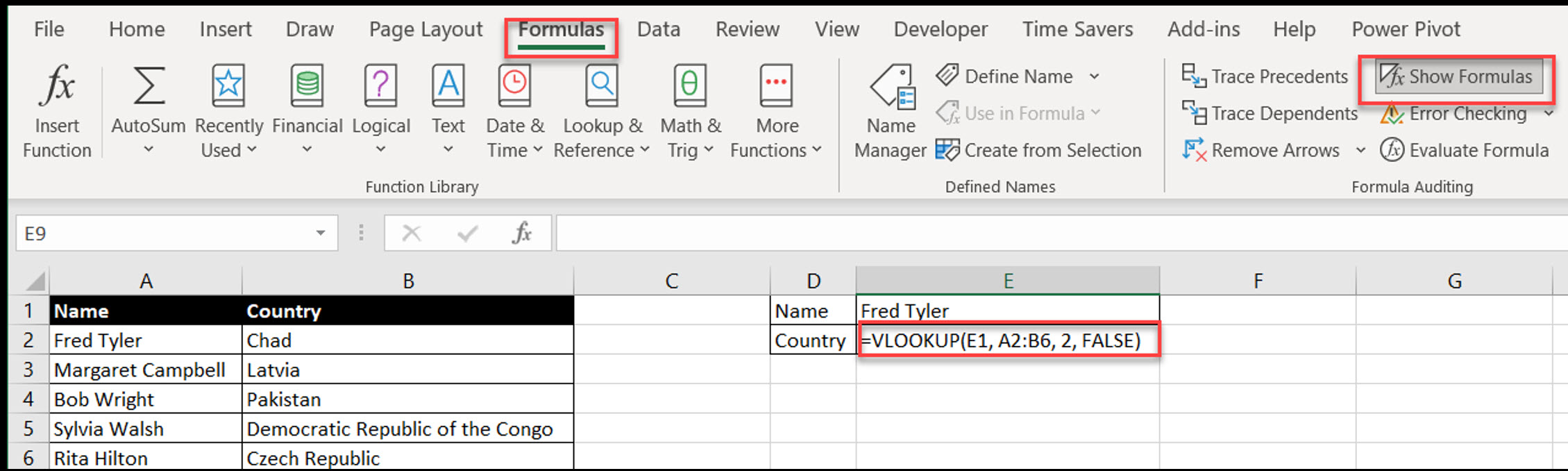
Purpose: Show all formulas in the worksheet instead of their results.
How to:
Go to Formulas > Show Formulas, or
Press Ctrl + ~ (tilde)
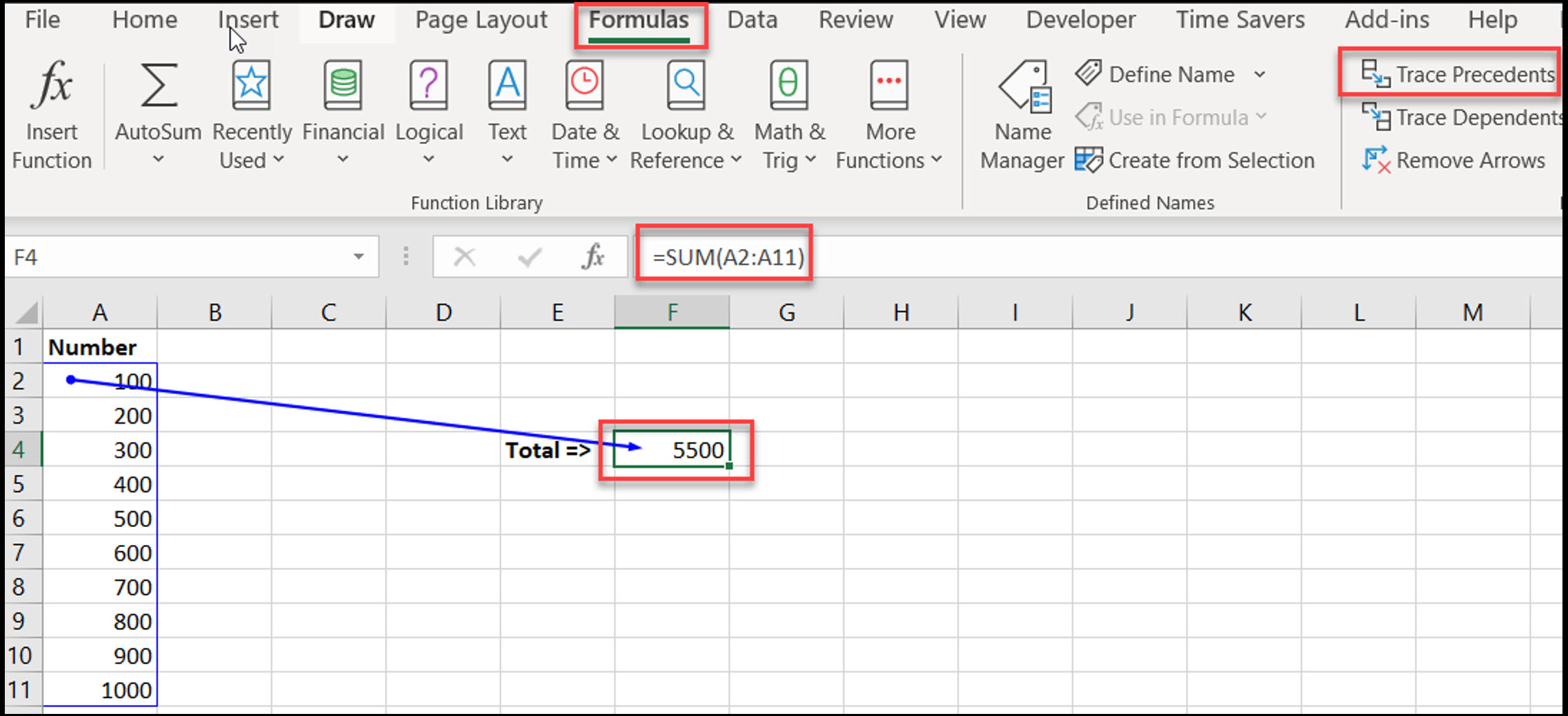
How to:
Purpose: Find cells that are referenced in a formula (i.e. cells that affect the selected cell’s value).
Select the cell with the formula
Go to Formulas > Trace Precedents
Visual: Excel will draw arrows to the cells used in the formula.
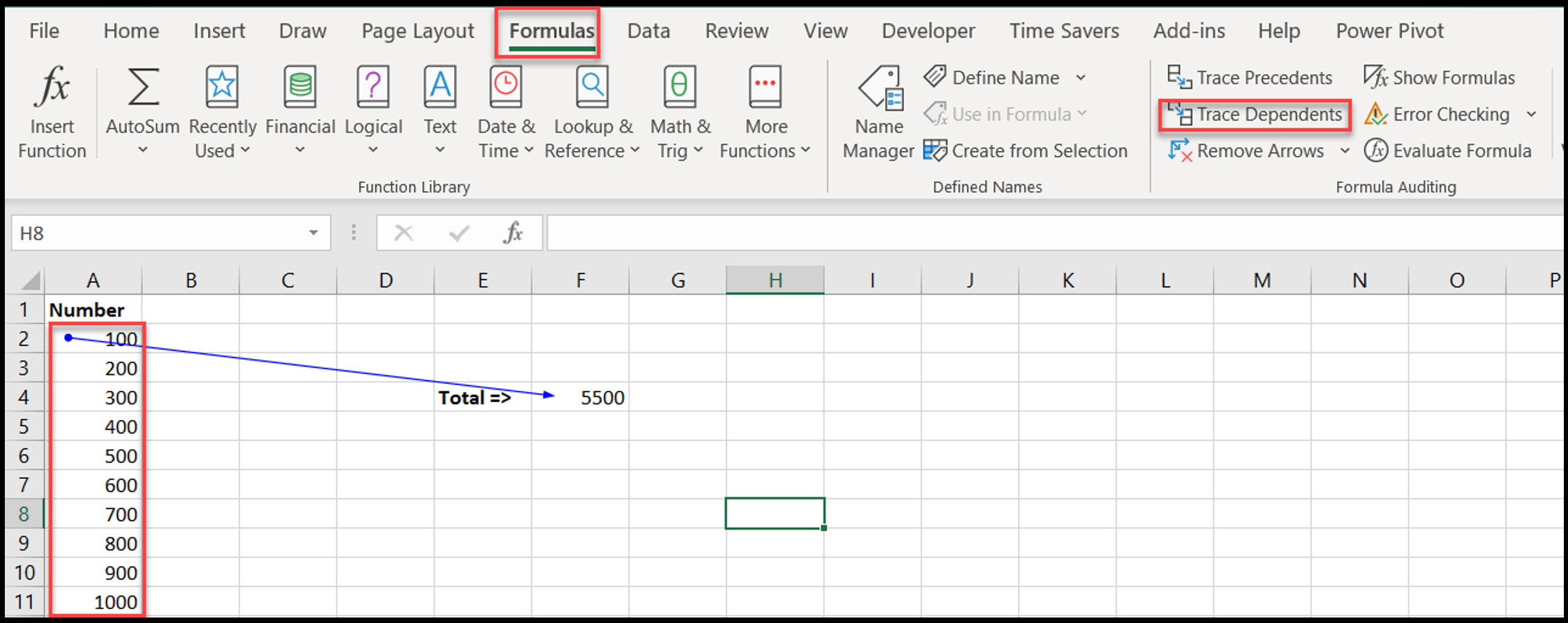
Purpose: Find cells that depend on the selected cell (i.e. cells that use the selected cell in their formulas).
How to:
Select the cell you want to check
Go to Formulas > Trace Dependents
Visual: Arrows will point to cells that use the selected cell in their formulas.
Purpose: Find and fix Excel errors.
How to turn on:
Go to File > Options > Formulas
Check “Enable background error checking”
Click OK
How to:
Go to Formulas > Error Checking
Review and fix each error
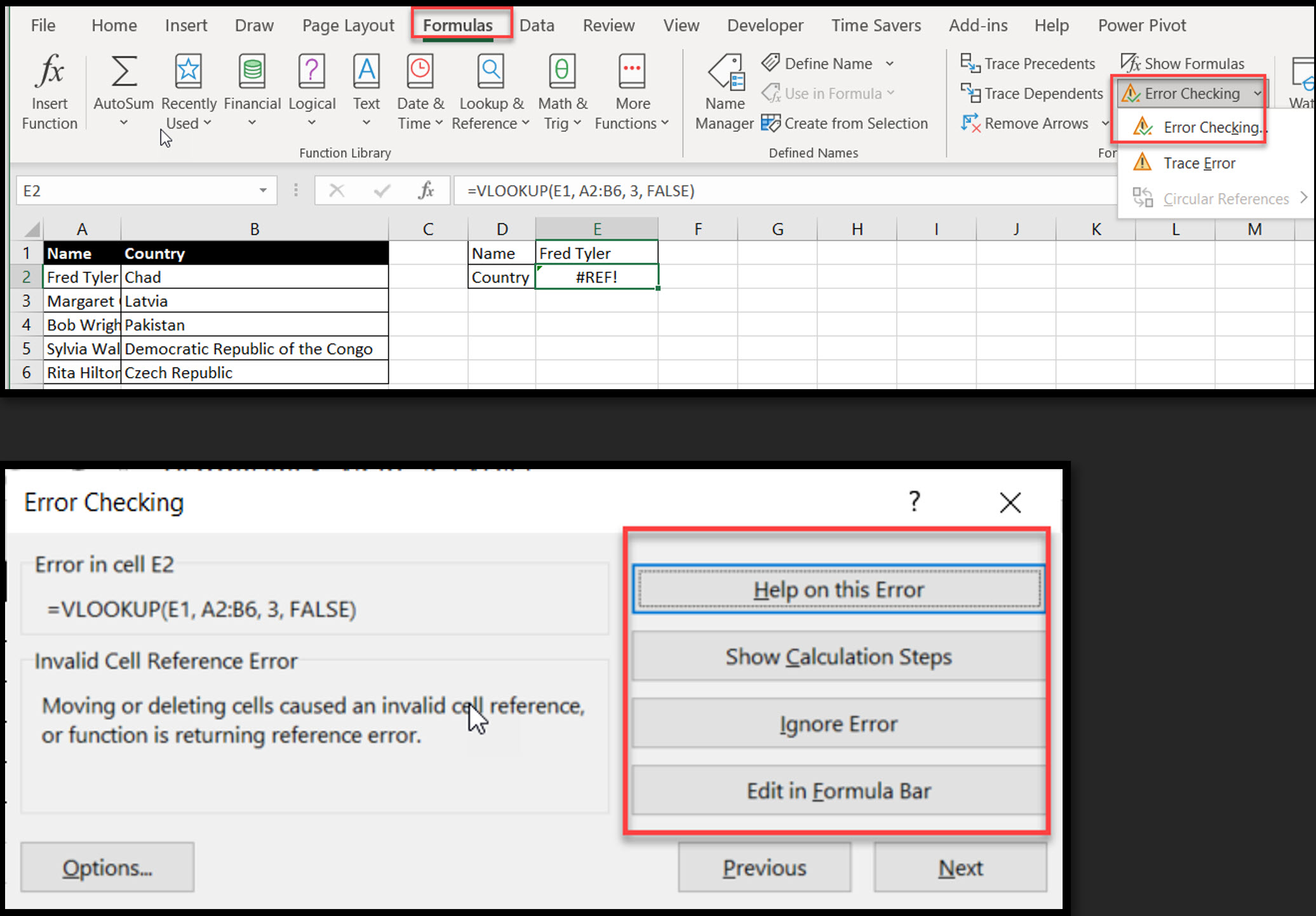
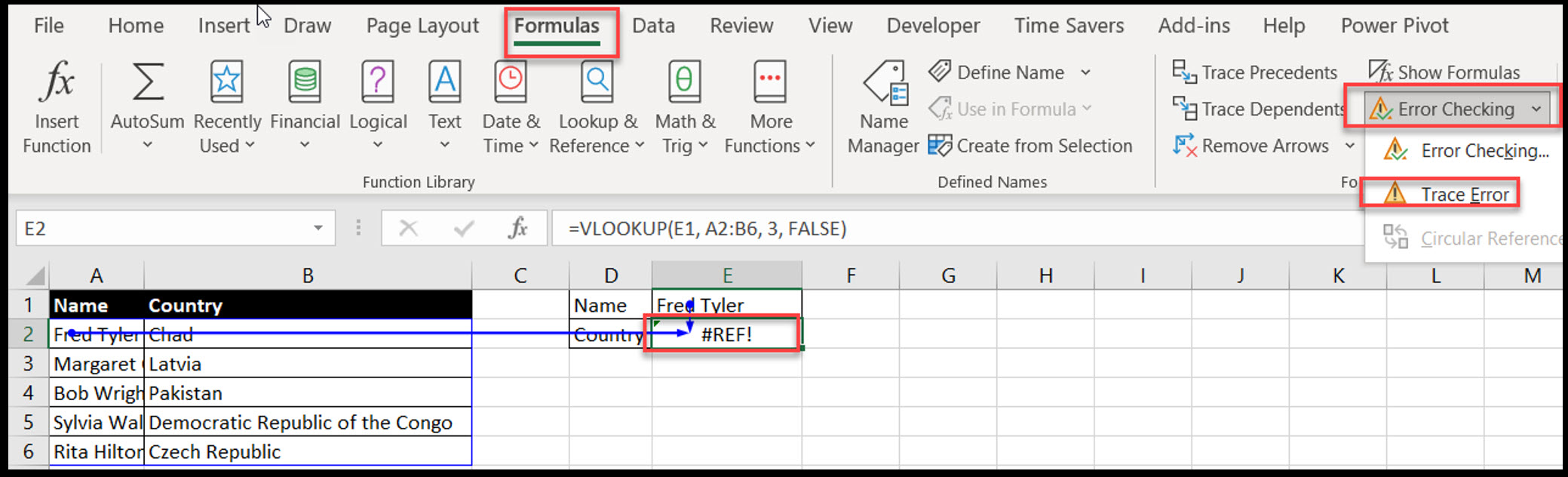
Purpose: Find the source of an error in a formula by tracing its precedents to fix Excel errors.
How to:
Select a cell with an error
Go to Formulas > Error Checking > Trace Error
Visual: Excel will draw arrows to the cells causing the error, so you can quickly see where the problem is.
Purpose: Debug complex or nested formulas by stepping through them to fix Excel errors.
How to:
Select the cell with the formula
Go to Formulas > Evaluate Formula
Click “Evaluate” to step through the formula

Advanced Excel formula troubleshooting requires a deeper understanding of Excel formulas and functions. Here are some advanced techniques to help you troubleshoot complex formulas:
The IFERROR function can be used to return a value if an error occurs in a formula. This is particularly useful for handling errors gracefully and preventing them from disrupting your calculations.
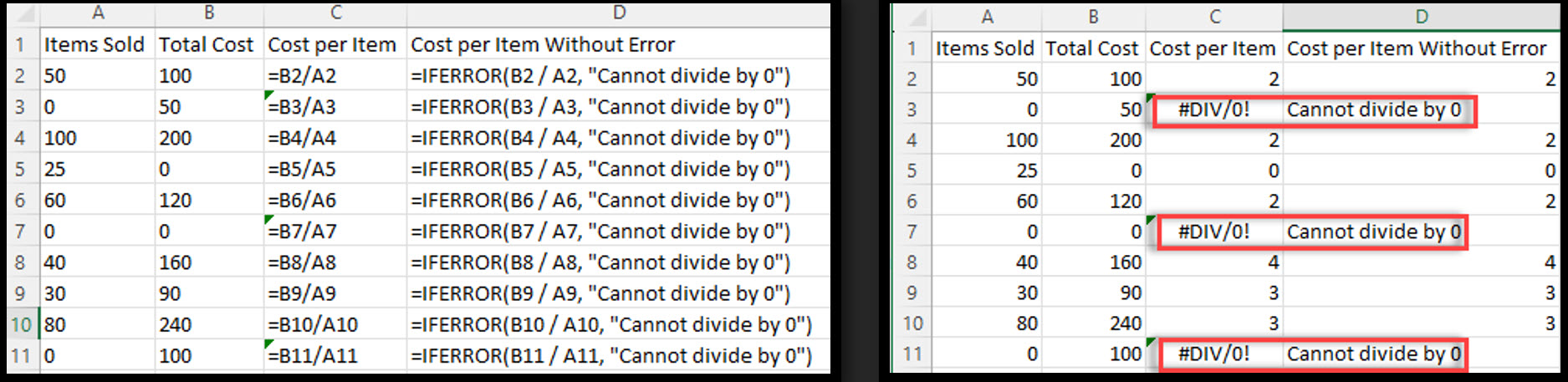
Example 1 - #DIV/0! Error
Suppose you have a list of items sold and their respective costs. You want to calculate the cost per item, but some rows have zero items sold, which would result in a #DIV/0! error.
By using IFERROR, you can return a custom message or value instead of the error.
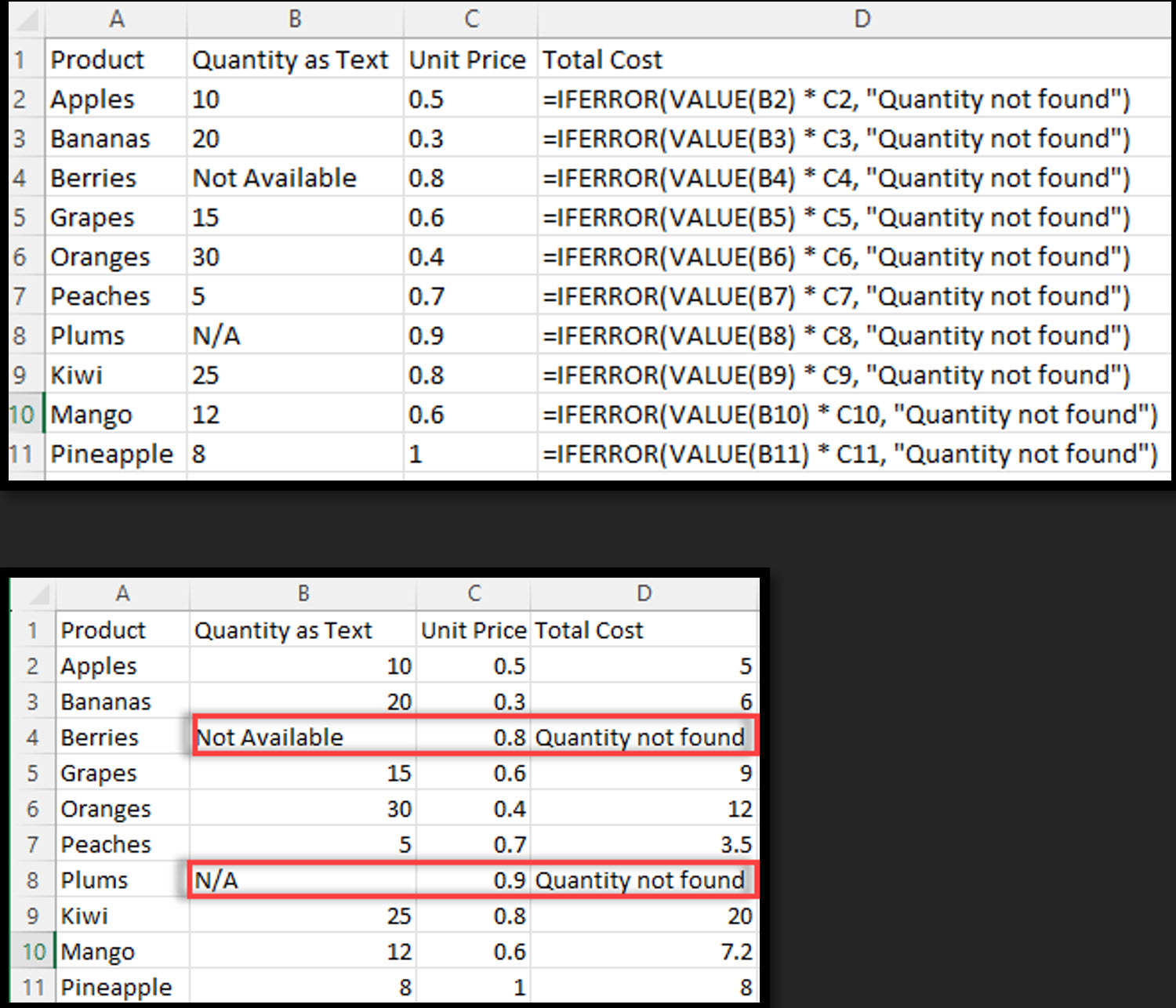
Example 2 - VALUE! Error
You have a list of products with quantities represented as text, and you want to calculate the total cost by multiplying the quantity by the unit price. The VALUE function can convert the text to numbers, but if it encounters text that can’t be converted to numbers, it returns a #VALUE! error.
By using IFERROR, you can return a custom message or value instead of the error.
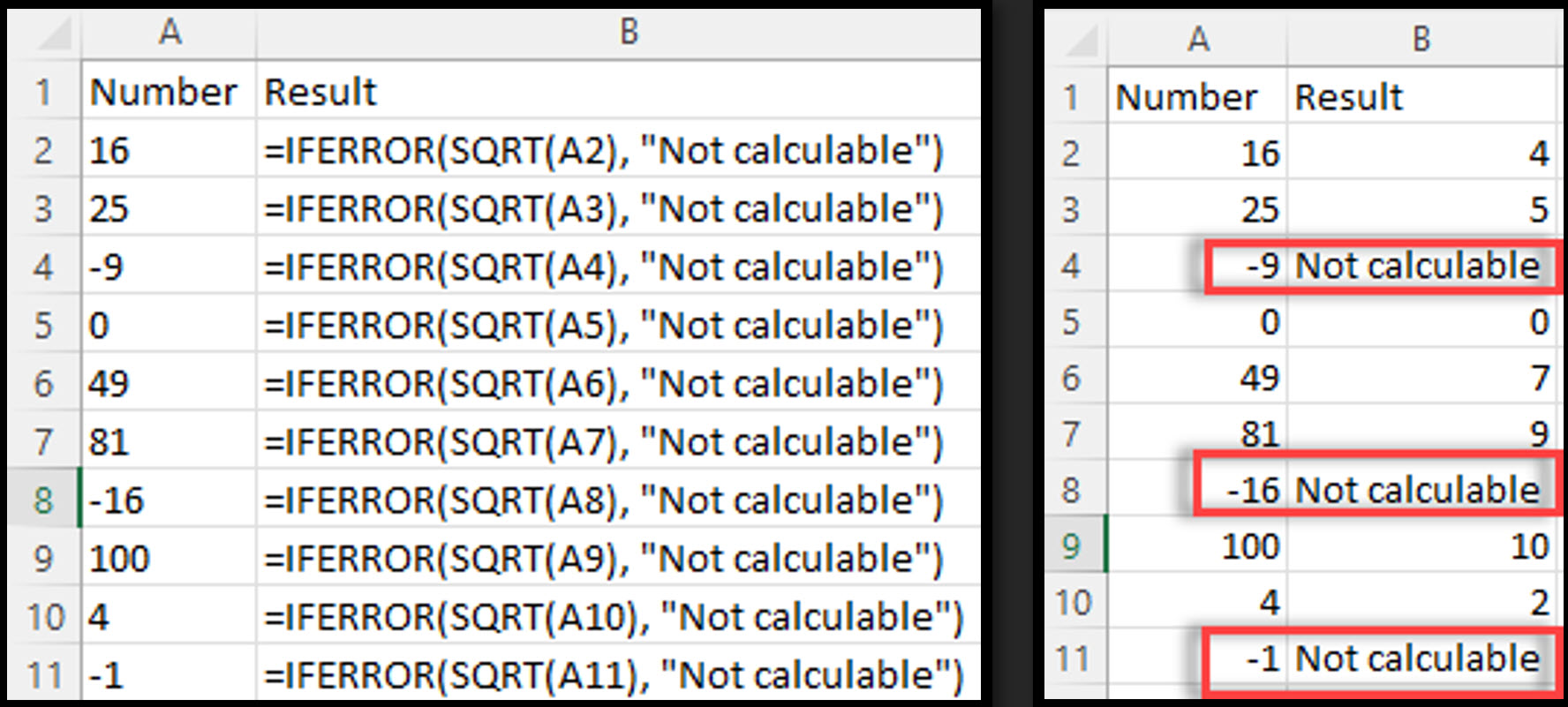
Example 3 - #NUM! Error
You have a list of numbers and want to calculate each number’s square root. When a number is negative, the SQRT function will return a #NUM! error.
By using IFERROR, you can return a custom message or value instead of the error.
Check your IF syntax: =IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false). Ensure all arguments are present and correctly formatted. Verify cell references and data types match the expected inputs.
A formula error occurs when Excel cannot calculate a result due to incorrect syntax, invalid references, or incompatible data types. Common errors include #NAME?, #DIV/0!, #VALUE!, #REF!, and #N/A.
To fix a reference error:
Check for deleted or moved cells/sheets
Verify absolute/relative references are correct
Ensure external file links are valid
Use the “Trace Error” feature to identify problematic cells
To remove an error:
Identify the cause using error indicators or Trace Error
Correct the underlying issue (syntax, references, data types)
Use error handling functions like IFERROR() to display alternate values
To disable error checking:
Go to File > Options > Formulas
Under “Error checking rules,” uncheck specific rules or “Enable background error checking”
Note: It’s generally better to fix errors than disable checking.
To fix a #VALUE error:
Ensure all referenced cells contain the correct data type
Check for text in numerical calculations
Verify date formats are consistent
Use appropriate conversion functions (e.g., VALUE(), TEXT())
When a formula refers to an incorrect cell reference, Excel may return errors like #REF!, which indicates that the cell reference is invalid, often due to deletion or improper linking.
Mastering Excel’s Formula Auditing tools is crucial for creating and maintaining accurate, efficient, and error-free spreadsheets. By understanding common formula errors and utilizing the powerful auditing features, you can quickly identify and resolve issues in your Excel workbooks, saving time and reducing frustration.
Regular use of these tools will not only improve the quality of your work but also enhance your overall Excel skills, making you a more proficient and confident user. As you become more familiar with these techniques, you’ll find yourself creating more robust and reliable spreadsheets, capable of handling even the most complex data analysis tasks.

92% of students automate workflows, build CEO-ready dashboards, and streamline collaboration in < 1 hour. Don’t miss out!
🎯Master every Office 365 tool like Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Teams, Outlook and OneNote.
🎯Streamlined approach—no fluff, just rapid skill-building.
🎯Eliminate tedious tasks with intelligent automation.
🎯Transform everyday workflows into strategic power moves.
🎯Boost productivity and impress every boss.
🎯Real-World Projects – directly translate lessons into workplace wins.