Got a messy spreadsheet with empty rows? Learn how to remove empty rows excel blank rows. This post will walk you through simple steps, shortcuts, and answers to your questions so data management is a breeze.
by Mihir Kamdar / Last Updated:
After reading this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to:
Download our step-by-step tutorial file now by clicking on the icon below and follow along to enhance your Excel skills practically and efficiently!
We’ve all been there—digging through an Excel spreadsheet only to be frustrated by all the empty rows that make your data look messy and harder to work with. Whether you’re managing a small budget or huge datasets, those blank rows can slow you down and make tasks like sorting, filtering, or creating pivot tables a pain. But don’t worry! In this post we’ll go through how to delete empty rows in Excel using different methods for different needs and skill levels. By the end you’ll have a clean, streamlined spreadsheet that’s easy to use and navigate.
When working with large data sets in Excel, it can be frustrating to see empty rows cluttering up your spreadsheet. Knowing how to remove empty rows in Excel can save time and improve the overall appearance and functionality of your data. Whether you want to remove blank rows in Excel or delete blank rows in Excel, there are simple methods you can apply. You might ask, “how do I delete blank rows in Excel?” or “how can I delete blank rows in Excel?” The good news is that Excel offers several tools to quickly eliminate those unwanted empty rows, whether it’s removing blank lines in Excel or deleting empty rows in Excel.
If you want to remove all blank rows in Excel or delete all blank rows in Excel, there are both manual and automated methods, such as using the hotkey to delete rows in Excel or utilizing Excel’s filtering features. Excel delete blank rows can be done efficiently with these techniques, ensuring that you don’t have to waste time sorting through each line. Whether you’re working on a cloud version or a desktop version of Excel, you can learn how to delete empty rows in Excel with ease. By following simple steps, you can remove blank rows in Excel, delete empty rows in Excel, and even eliminate empty rows in Excel with minimal effort.
Empty rows might seem harmless, but they can cause a bit of trouble in your Excel workflow:
Messy Data Analysis: Blank rows can mess up sorting, filtering, and pivot tables, leading to inaccurate results.
Larger File Sizes: Extra rows can make your Excel file bigger and slower to open and work with.
Less Readable: Clean data is easier to read and helps you spot trends or problems quickly.
Empty rows in Excel can be a nuisance, especially when working with large datasets. But what exactly constitutes an empty row? An empty row is a row that contains no data or cells with values. These rows can appear anywhere in your worksheet and are often caused by:
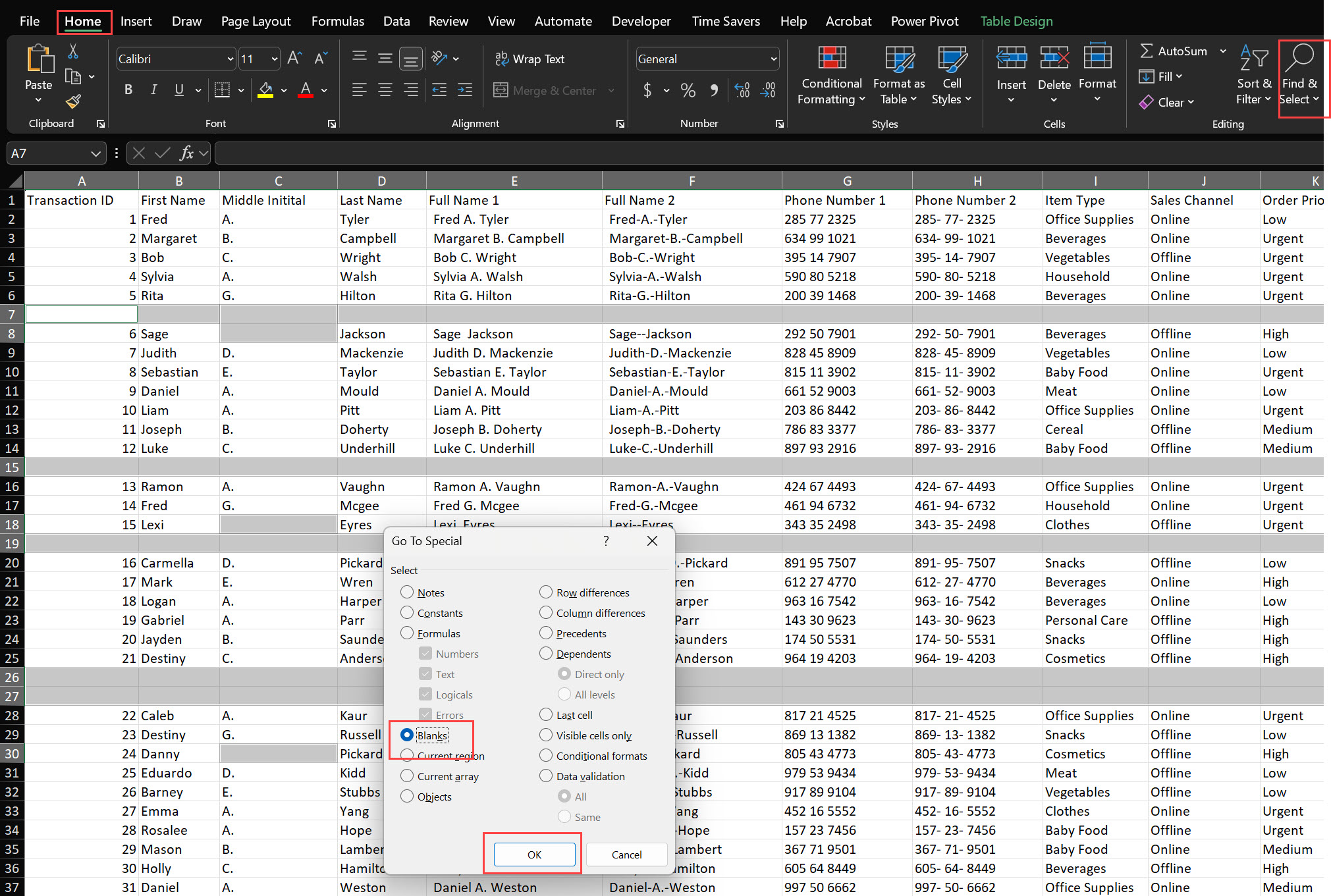
To identify and address empty rows, you can use Excel’s “Find & Select” feature. Follow these steps:
1. Open the Find & Select Menu:
2. Use Go To Special:
3. Highlight Blank Cells:
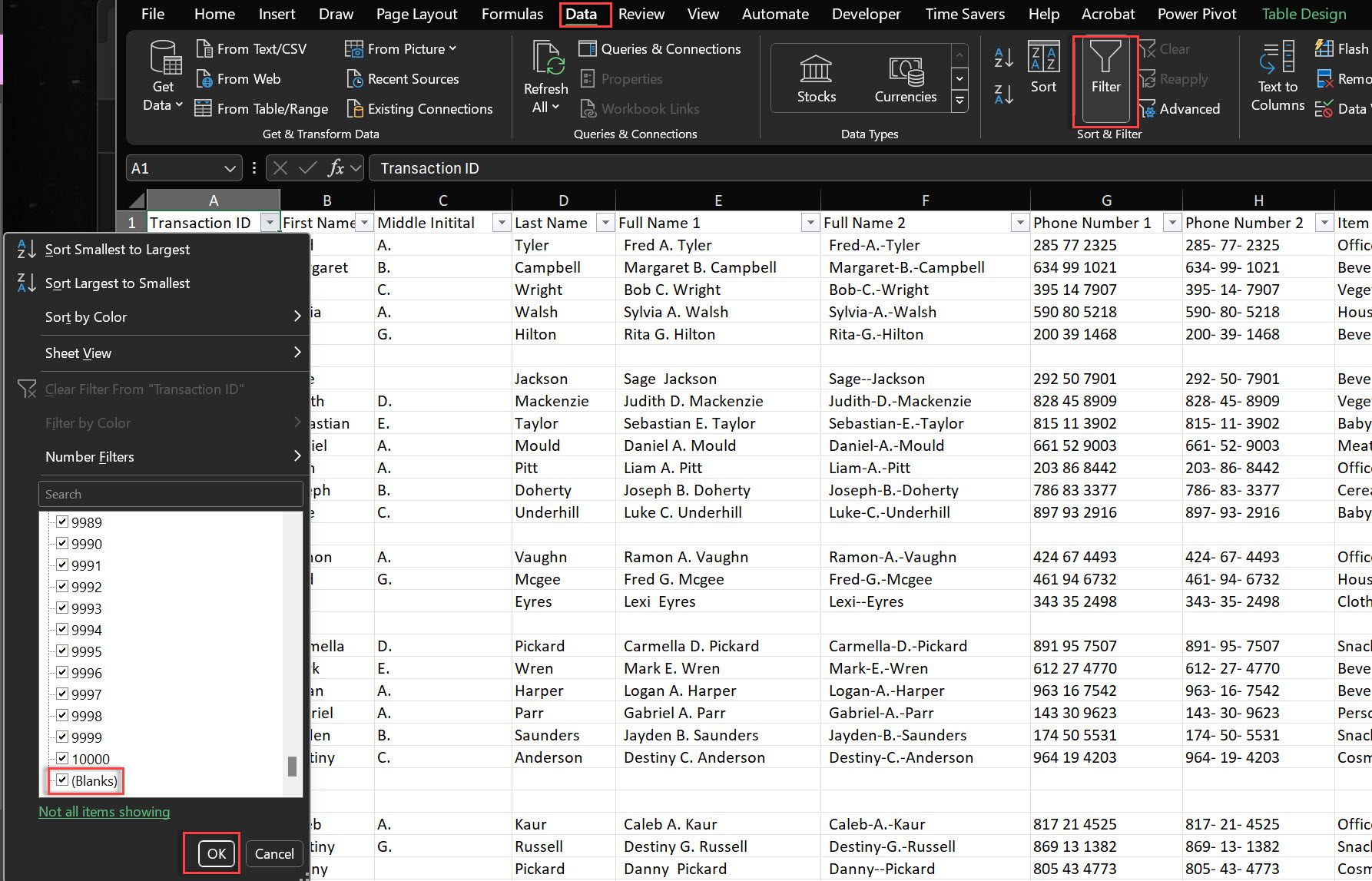
The easiest way to delete blank rows in Excel is by using the Filter. It’s simple and doesn’t require advanced Excel skills.
Steps:
1. Select Your Data Range:
Ctrl + A to select all.2. Apply Filters:
3. Filter Blanks:
4. Delete Blank Rows:
5. Clear Filters:
This method is great for quick deletion of blank rows without disturbing the rest of your data.
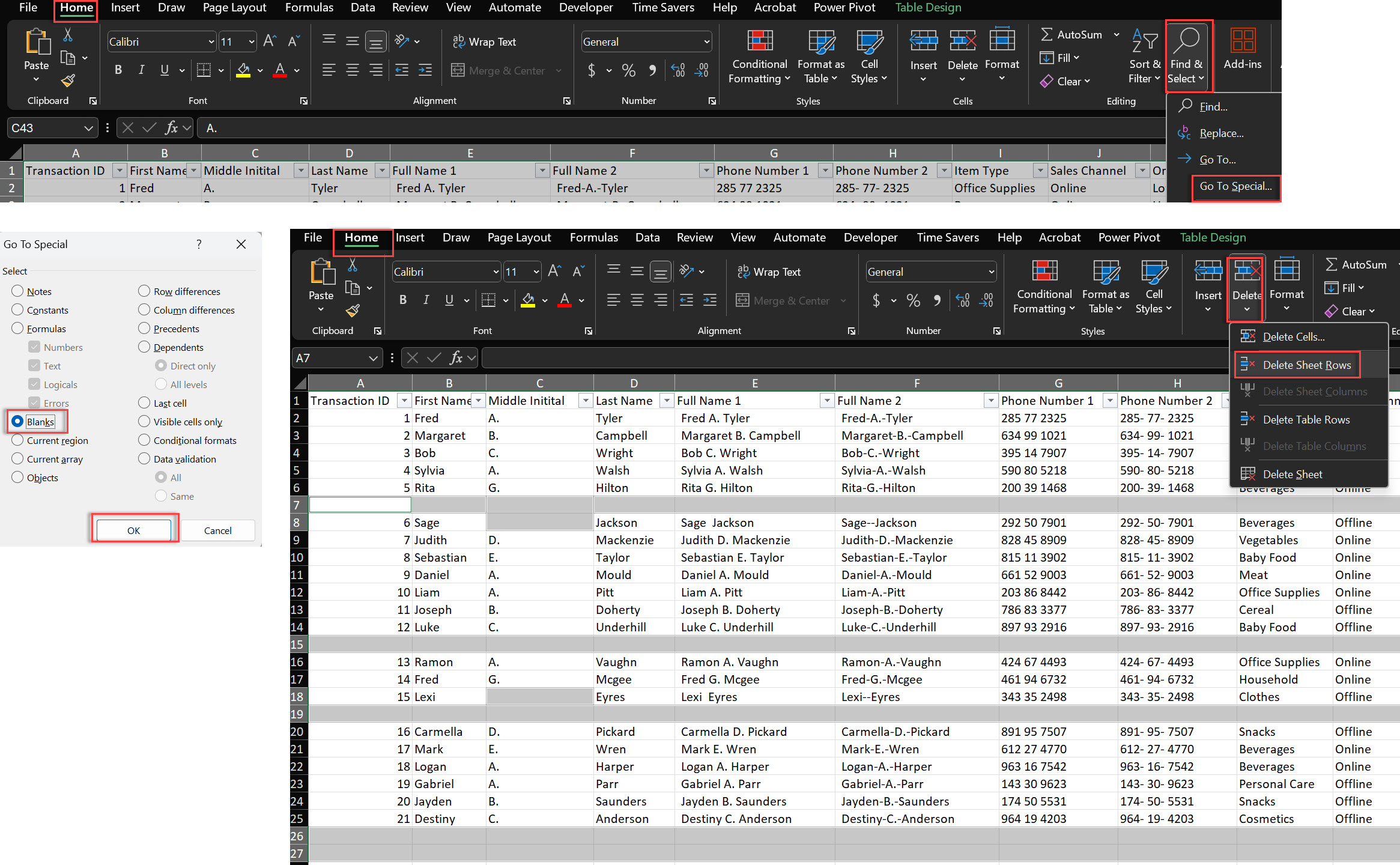
If you have a large dataset, Go To Special can save you a lot of time when deleting blank rows in Excel.
1. Select Your Data Range: Select the range of cells where you want to remove blank rows.
2. Select the Blank Row’s Number: On the left side of the worksheet, select the number of the blank row you want to delete.
3. Go To Special: Press F5 to open the Go To dialog box > Click Special.
4. Select Blanks: In the Go To Special window, select Blanks and click OK > All blank cells in your selected range will be highlighted.
5. Delete Blank Rows: With the blank cells highlighted, go to the Home tab in your Excel worksheet > Click Delete > Delete Sheet Rows.
6. Confirm Deletion: Excel will delete all rows with the selected blank cells and clean up your data instantly.
This method is great when you have multiple columns involved and you want to delete only complete blank rows.
For those who love automation, using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) can make deleting empty rows in Excel a walk in the park, especially if you do it regularly.
Steps:
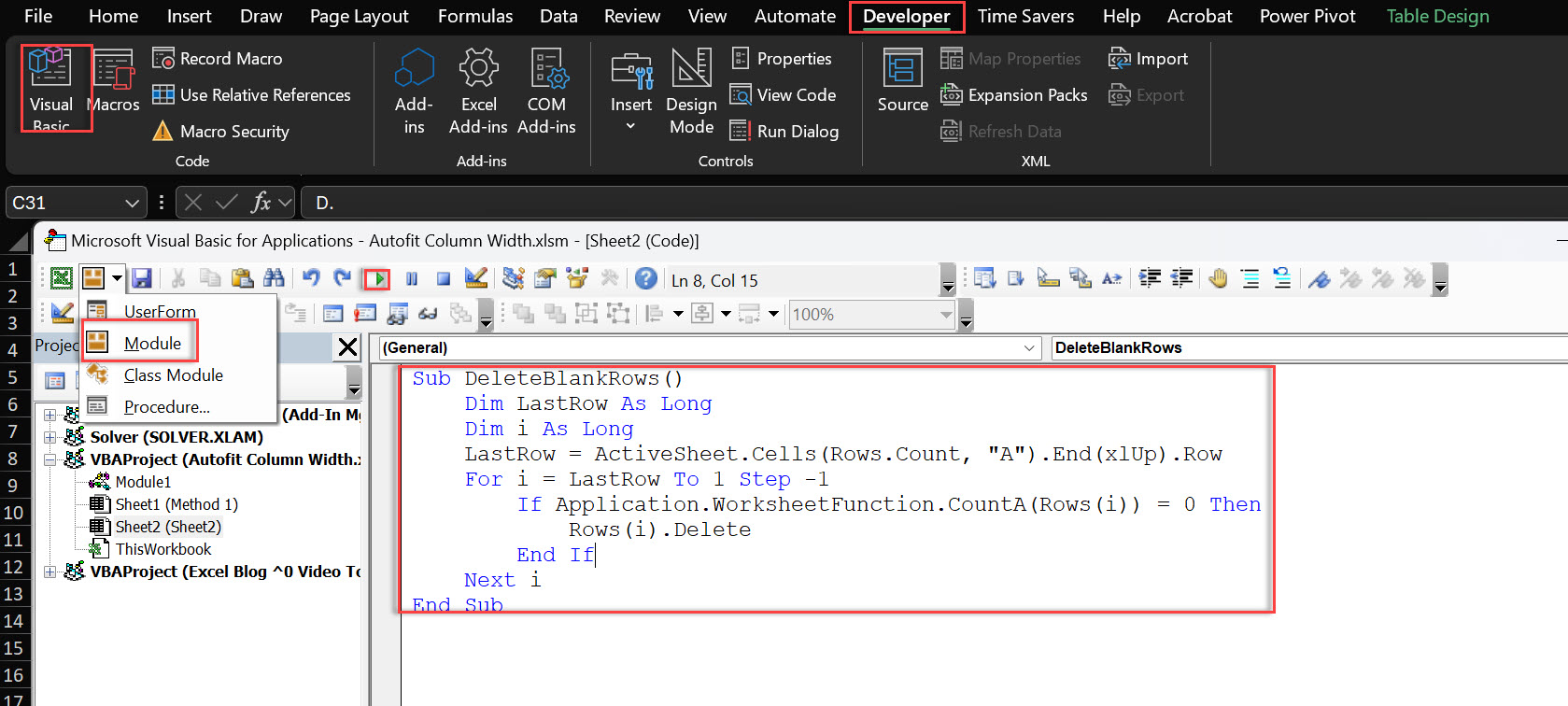
1. Open VBA Editor: Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
2. Insert a New Module: In the VBA editor, go to Insert > Module.
3. Paste VBA Code:
Sub DeleteBlankRows() Dim LastRow As Long Dim i As Long LastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row For i = LastRow To 1 Step -1 If Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Rows(i)) = 0 Then Rows(i).Delete End If Next i End Sub 4. Run the Macro: Press F5 while in the VBA editor, or go back to Excel, press Alt + F8, select DeleteBlankRows, and click Run.
This macro will scan each row and delete it if it’s completely blank. The VBA code will check the used range to identify and delete empty rows. It’s a great way to do repetitive tasks without lifting a finger!
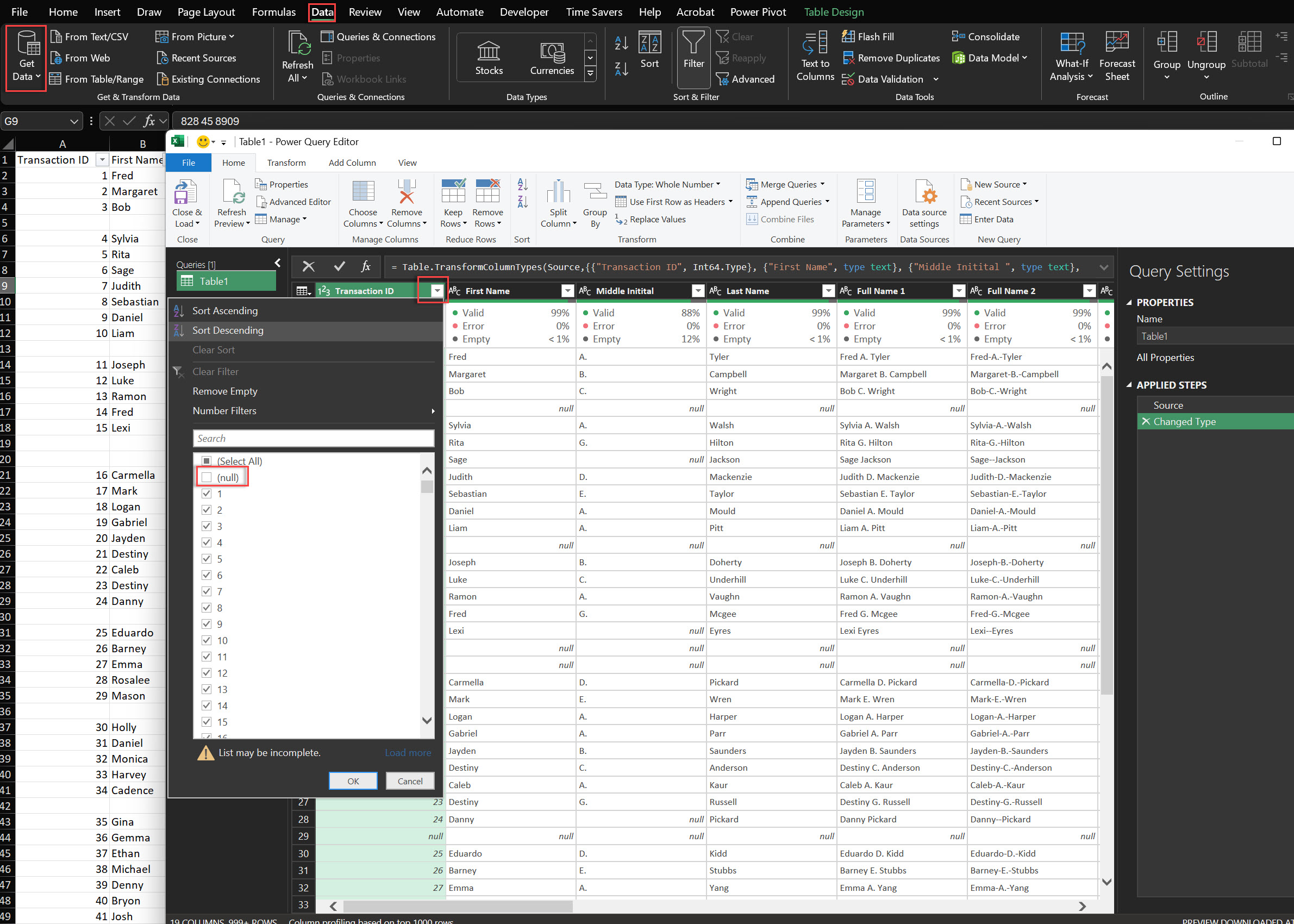
Power Query is a powerful tool in Excel that can help you delete blank rows easily, especially when working with external data sources.
Steps:
1. Load Data into Power Query: Select your data range > Go to the Data tab and click From Table/Range.
2. Remove Blank Rows: In the Power Query Editor, select the columns you want to check for blanks > Right-click on the selected columns and select Remove Empty.
3. Load Clean Data: Click Close & Load to load the clean data back into Excel.
Power Query is great for those who import data frequently and need a quick way to delete blank rows automatically.
Conditional Formatting: Highlight blank rows so you can see them before deletion.
Sort Your Data: Sorting can group all blank rows together so you can select and delete them easily.
Backup Your Data: Always backup before doing bulk deletion to avoid losing important information.
Combine Methods: Sometimes, using a combination of these methods works best, especially with complex data.
When deleting rows in Excel, it’s essential to follow best practices to avoid accidentally deleting important data. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
1. Select the Entire Row: Always select the entire row by clicking on the row number, rather than selecting individual cells. This ensures that you delete the entire row and not just parts of it.
2. Use the Delete Sheet Rows Feature:
3. Be Cautious with Formulas and Formatting:
4. Use the Undo Feature:
Ctrl + Z) to recover any accidentally deleted data.By following these best practices, you can ensure that you delete rows safely and efficiently, keeping your data intact and your worksheet organized.
Deleting thousands of blank rows manually is tedious, but here are two efficient methods:
Using Go To Special:
F5, click Special, select Blanks, and click OK.Using VBA:
Alt + F11. Sub DeleteAllBlankRows() On Error Resume Next Columns("A").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks).EntireRow.Delete On Error GoTo 0 End Sub Both methods are fast and efficient for handling large numbers of blank rows.
To delete rows that are entirely blank:
Steps:
1. Select Entire Sheet: Click on the top-left triangle or press Ctrl + A to select the sheet, ensuring you have the correct blank row’s number.
2. Go To Special: Press F5, click Special, select Blanks, and click OK.
3. Delete Entire Rows: Right-click on any blank cell and choose Delete > Entire Row.
This will delete only completely blank rows and not the partially filled ones.
There’s no single shortcut, but you can use this combination:
Select Data Range: Press Ctrl + A.
Go To Special: Press F5, then Alt + S.
Blanks: Press K and then Enter.
Delete Rows: Press Ctrl + -, choose Entire Row, and press Enter.
This uses keyboard shortcuts to speed up the deletion process.
1. Select Data Range: Highlight the range with blank cells you want to remove.
2. Go To Special: Press F5, click Special, select Blanks, and click OK.
3. Shift Cells Up: Right-click on any blank cell > Choose Delete, select Shift cells up, and click OK.
This will remove blank cells and shift the rest of the data up, keeping your dataset structure intact.
When deleting rows in Excel, there are several common mistakes to avoid. Here are some of the most frequent pitfalls:
1. Deleting Rows by Selecting Blank Cells:
2. Not Selecting the Entire Row:
3. Not Using the Delete Sheet Rows Feature:
4. Not Checking for Formulas or Formatting:
5. Not Using the Undo Feature:
Ctrl + Z) to recover any accidentally deleted data.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that you delete rows safely and efficiently, keeping your data clean and your worksheet organized.
Removing empty rows from your Excel sheets is crucial to keep your data organized and efficient. Whether you use built-in features like Filter and Go To Special, automate the process with VBA, or use Power Query, there’s a method that suits your workflow. And knowing how to handle thousands of blank rows, delete completely blank rows, use shortcuts, automate deletions, remove blank cells from rows, and even delete rows randomly will make you a data management master. By using these techniques, your Excel files will be tidy, easy to navigate, and optimized for data analysis.

92% of students automate workflows, build CEO-ready dashboards, and streamline collaboration in < 1 hour. Don’t miss out!
🎯Master every Office 365 tool like Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Teams, Outlook and OneNote.
🎯Streamlined approach—no fluff, just rapid skill-building.
🎯Eliminate tedious tasks with intelligent automation.
🎯Transform everyday workflows into strategic power moves.
🎯Boost productivity and impress every boss.
🎯Real-World Projects – directly translate lessons into workplace wins.