ower Pivot allows you to model and work with large data sets, while DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) brings advanced calculation capabilities to your fingertips. Together, they empower you to turn raw data into meaningful insights, streamline reporting, and drive smarter decision-making. Ready to unlock the full potential of your data? This guide will walk you through the essentials.
by Mihir Kamdar / Last Updated:
If you read this guide, you will learn the whole of Power Pivot and how it can transform Excel. Here’s what we’ll cover in detail:
Download our step-by-step tutorial file now by clicking on the icon below and follow along to enhance your Excel skills practically and efficiently!
Power Pivot is an add-in for Microsoft Excel that changes the way we manage and analyze data. When working with large datasets with millions of rows, traditional Excel tools can be a challenge. However, Power Pivot allows Excel to scale up, so you can explore, model, and analyze data at a large scale with no performance penalties. Power Pivot gives users access to advanced data modeling tools, which would otherwise hide insights.
Power Pivot takes things beyond the standard Excel features by allowing you to manage your data as if it were a database, multi-table data models, relationship building, and complex calculations using DAX. The features of this add-in make it invaluable for business analysts, data scientists, financial professionals, and anyone who needs to do robust data analysis in Excel.
Using Power Pivot, Excel becomes a data analytics and business intelligence platform. In this guide, we will learn about the core functionalities of Power Pivot and how you can use them to handle data, discover trends, and make informed decisions based on insights.
Microsoft Power Pivot, combined with Power Query, allows users to create sophisticated data models and unlock powerful data analysis capabilities within an Excel workbook. Power Query simplifies data extraction and transformation, enabling seamless data manipulation capabilities from various sources.
Once integrated into the Power Pivot gallery, these data models provide a robust foundation to perform powerful data analysis and gain insights quickly. With these tools, users can efficiently manage large datasets, perform complex calculations, and perform information analysis rapidly, making Microsoft Power Pivot a game-changer for Excel users seeking advanced analytics solutions.
Power Pivot in Excel is a powerful tool that allows users to get data from Power Pivot to Excel effortlessly, enabling more advanced data manipulation and analysis. It enhances your ability to create complex pivot tables and efficiently analyze large datasets, making it a must-have feature for anyone working with data in Excel.
If you’re looking to work with historical data, such as calculating the average of 4 years of data in Power Pivot, this tool simplifies the process with its robust calculations. Additionally, Power Pivot is closely integrated with Power BI, offering users the ability to create dynamic pivot tables in Power BI to visualize and analyze data more effectively.
For those exploring more about data modeling, dimensions in Power Query Power Pivot are key concepts that allow users to structure their data for better analysis. Whether you’re an Excel user or looking to transition to Power BI, Power Pivot tables are an essential feature for handling complex datasets.
Power Pivot and Power Query are two powerful tools in Excel that cater to different aspects of data handling. Power Query is primarily used for importing, transforming, and cleaning data, while Power Pivot allows users to create relationships between data sets, perform advanced calculations, and build sophisticated data models. If you’re wondering what Power Pivot is, it’s an Excel feature that enhances data analysis by enabling you to manage large datasets efficiently and perform complex calculations.
To get started, you need to know how to add Power Pivot to Excel. Go to the Options menu, select Add-ins, and activate the Power Pivot add-in from the COM Add-ins list. Once enabled, you can explore how to use Power Pivot by loading data into the model, creating relationships, and generating insightful pivot tables.
While traditional pivot tables are great for basic summaries, Power Pivot extends capabilities, allowing advanced analytics and larger data sets. This difference is key when comparing Power Pivot vs. Pivot Table. Similarly, in Power BI, Power Pivot’s features integrate seamlessly to enhance pivot functionality in Power BI.
For those who work extensively with data in Excel, Power Pivot in Excel is an indispensable tool for creating robust data models and enabling powerful, actionable insights.
Power Pivot is a game-changing tool for Excel users who need to handle large datasets, perform advanced data analysis, and create sophisticated data models. If you’re asking when should you use Power Pivot, it’s most beneficial when you’re working with complex data that requires building relationships between multiple tables or creating calculated columns and measures. To access Power Pivot in Excel, you need to add Power Pivot to Excel via the Excel add-in Power Pivot. If you’re not sure how to get Power Pivot in Excel, simply navigate to the “File” tab, select “Options,” and enable the add-in from the “Manage Add-ins” menu.
Once you’ve installed it, learning how to use Excel Power Pivot can seem challenging, but there are many resources available, including Power Pivot tutorials to guide you. As you dive in, you’ll learn how to create Power Pivot pivot tables, which provide more flexibility and power compared to traditional Excel pivot tables. These tables allow you to analyze and summarize large amounts of data rapidly. Additionally, Power Pivot measures allow you to perform sophisticated calculations like sums, averages, and even custom formulas that you can use in your data analysis.
For users who prefer to work with cloud-based tools, Power Pivot vs Power BI is an important comparison. While Power Pivot is a powerful add-in for Excel that handles data manipulation within your workbook, Power BI provides a full suite of tools for business intelligence, including more advanced data visualization features. However, when working in Excel, Power Pivot tables are ideal for summarizing and analyzing data without the need for additional visualization tools.
For Excel users on a Macbook, it’s important to note that Power Pivot Mac is not available, limiting the functionality compared to the Windows version. If you’re asking what is Power Pivot in Excel, it’s a feature designed to enhance Excel’s data analysis capabilities by providing tools to create data models and perform calculations that go beyond basic Excel functionality. Whether you’re new to Power Pivot or a seasoned user, this add-in is an invaluable resource for anyone looking to perform powerful data analysis and gain deeper insights from their data.
Power Pivot was introduced as an Excel add-in in 2010 to enable data manipulation on a larger scale than Excel natively allowed. At its core is the Vertipaq engine, an in-memory technology designed to compress and manage large datasets. This allows Power Pivot to perform computations quickly, even when handling millions of rows, and makes it particularly useful in data-heavy industries like finance, retail, and manufacturing.
Power Pivot for 2010 & 2013
In Excel 2010 and 2013, Power Pivot must be downloaded separately and activated through the COM Add-ins menu. Once it’s installed, you have enabled COM Add-ins from File > Options > Add-Ins > COM Add-ins > Select Power Pivot > Press OK.
Power Pivot for 2016, 2019, 2021 & Office 365
In Excel 2016, 2019, 2021, and Office 365, it’s built-in, requiring only activation from File > Options > Add-Ins > COM Add-ins > Select Power Pivot > Press OK.
Power Pivot offers several benefits, including:
Through Power Pivot, users gain a level of analytical power and flexibility that makes Excel suitable for even the most data-intensive projects.
Power Pivot is a comprehensive tool for data modeling and in-depth analysis within Excel. It enables users to import data from various sources, transform it, and structure it into a cohesive model by establishing relationships between tables. With Power Pivot, you can create calculated columns and define custom measures using DAX (Data Analysis Expressions), enhancing data analysis beyond standard Excel capabilities. The results can be displayed in a PivotTable for detailed reporting or visualized in a PivotChart for graphical insights.
Power Pivot Components
While traditional PivotTables are limited to a single data source, Power Pivot’s Data Model PivotTable can pull in data from multiple tables and perform calculations at various levels. This flexibility lets users build a cohesive model that reflects complex business structures, such as multi-channel sales pipelines, supply chain networks, or regional sales performances.
Examples:
| Feature | Standard PivotTable | Data Model PivotTable |
| Custom Calculations | Limited to basic calculations | Supports advanced DAX calculations |
| Multiple Tables | Operates on a single table | Combines multiple tables in a data model |
| Data Size | Limited to ~1 million rows | Handles millions of rows without performance issues |
| Granularity | Supports basic, single-level analysis | Multi-level analysis for more detailed insights |
| Formatting Consistency | Manually applied to each PivotTable | Applies automatically when using the same measure |
| Reusability | Formulas cannot be reused across reports | DAX measures are reusable in multiple PivotTables |
| Performance | Slower with large datasets | Optimized for big data due to in-memory processing |
Power Pivot’s Data Model PivotTable is an invaluable tool for big data environments, offering scalability and efficiency that standard PivotTables lack.
To begin data analysis in Power Pivot, you first need to import data. Power Pivot supports data imports from various sources, including Excel tables, other Excel files, and Access databases. Once imported, these data sources combine into a cohesive Data Model, enabling unified analysis.
Real-world Applications:
Table Name | Source File | Table Type |
fct_SalesTransaction | Sales Transactions.xlsx | Fact Table |
dim_OrderPriority | Order Priority.xlsx | Dimension Table |
dim_SalesChannel | Sales Channel.xlsx | Dimension Table |
dim_Customer | Other Data.accdb | Dimension Table |
dim_Date | Other Data.accdb | Dimension Table |
dim_ItemType | Workbook Table | Dimension Table |
dim_Location | Other Data.accdb | Dimension Table |
In Power Pivot, data imports form the foundation for the entire model, supporting real-time updates, linked tables, and cross-referencing.
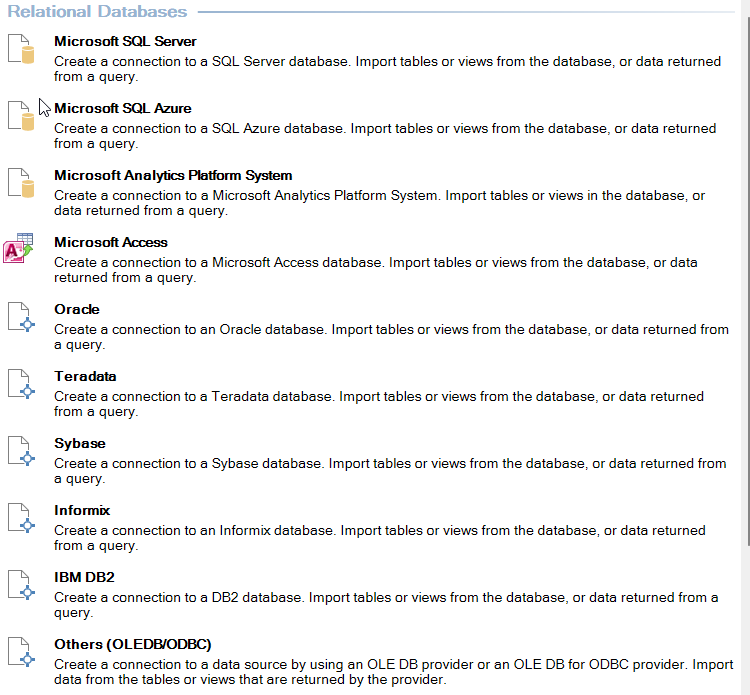
To import a table from Excel:
This simple step consolidates data within Power Pivot, ready for further analysis and manipulation.
Practical Example
Imagine a retail company importing inventory data as a table. By adding it to Power Pivot, they can link it to other tables such as Sales and Location, making it easy to calculate stock turnover rates, identify high-performing locations, and track demand trends.
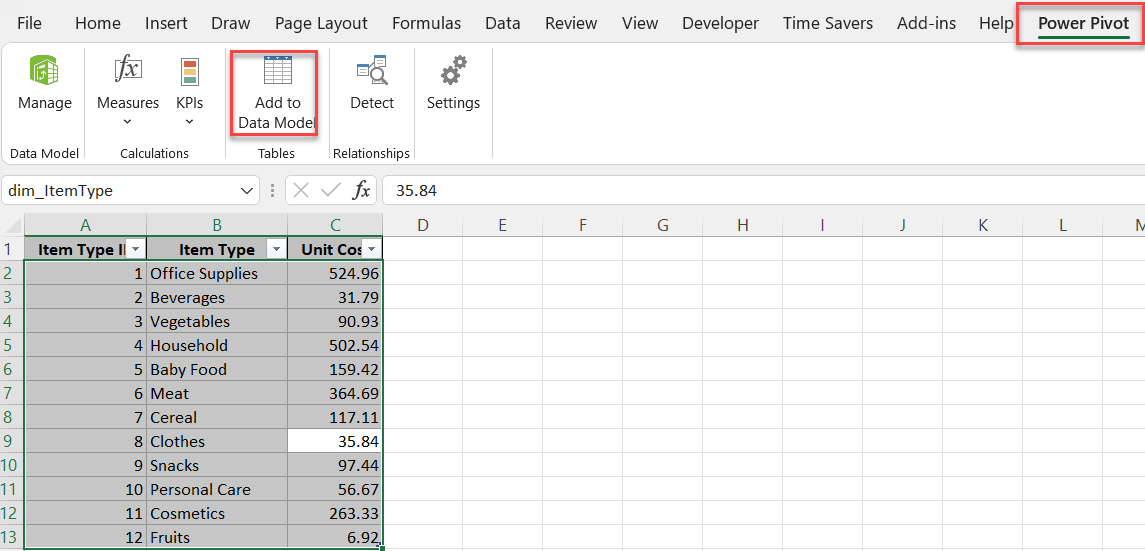
Power Pivot also supports importing entire Excel files. This feature is beneficial when consolidating data across multiple files or worksheets.
Step-by-Step:
Use Case
A company with monthly sales reports saved as separate Excel files can import all these files into Power Pivot, creating a unified dataset. This dataset can then be analyzed for seasonal trends, monthly growth, or other performance metrics.
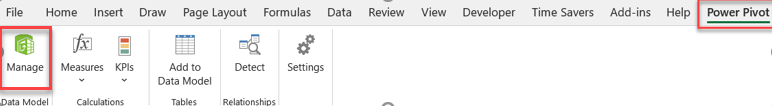
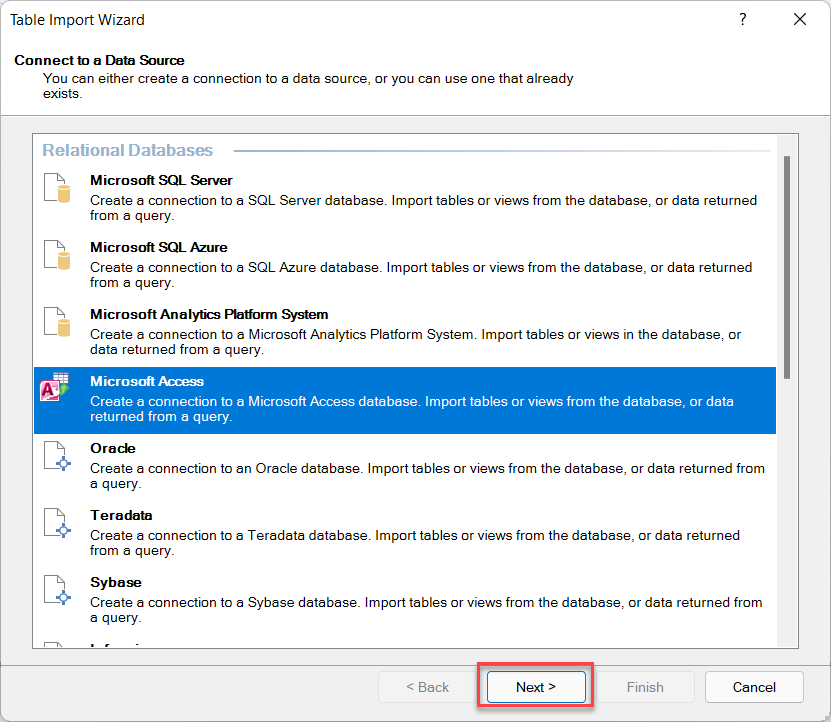
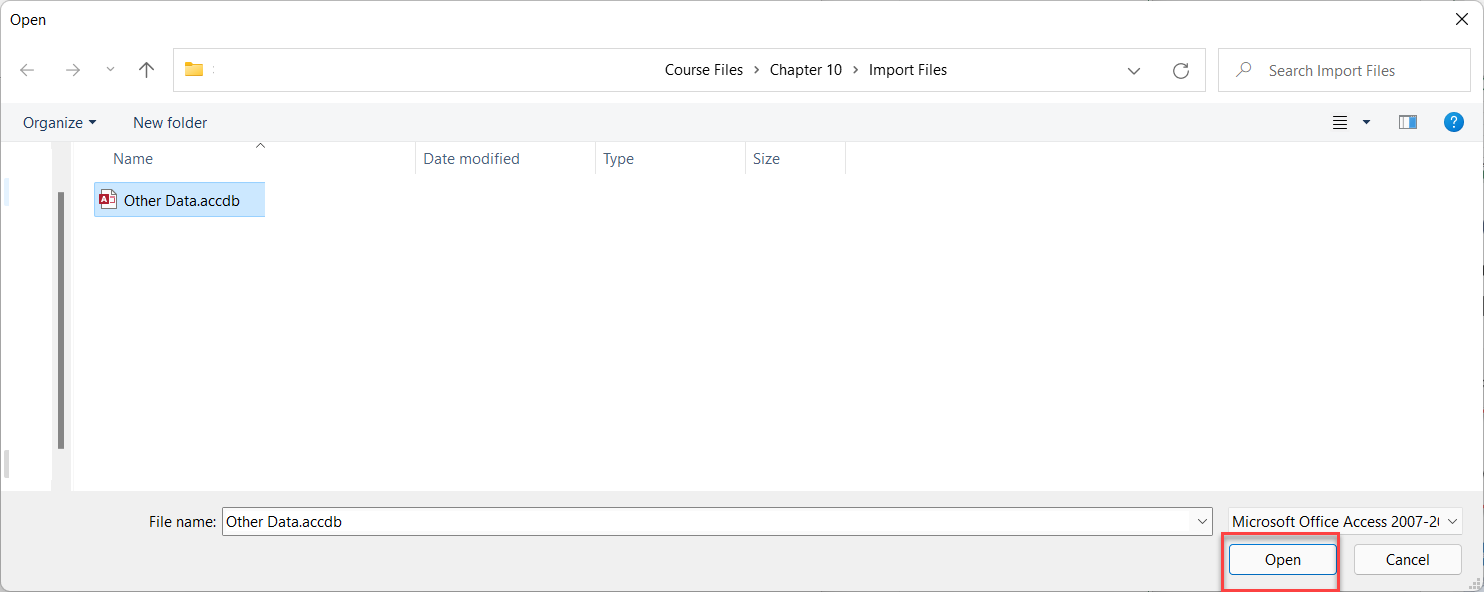
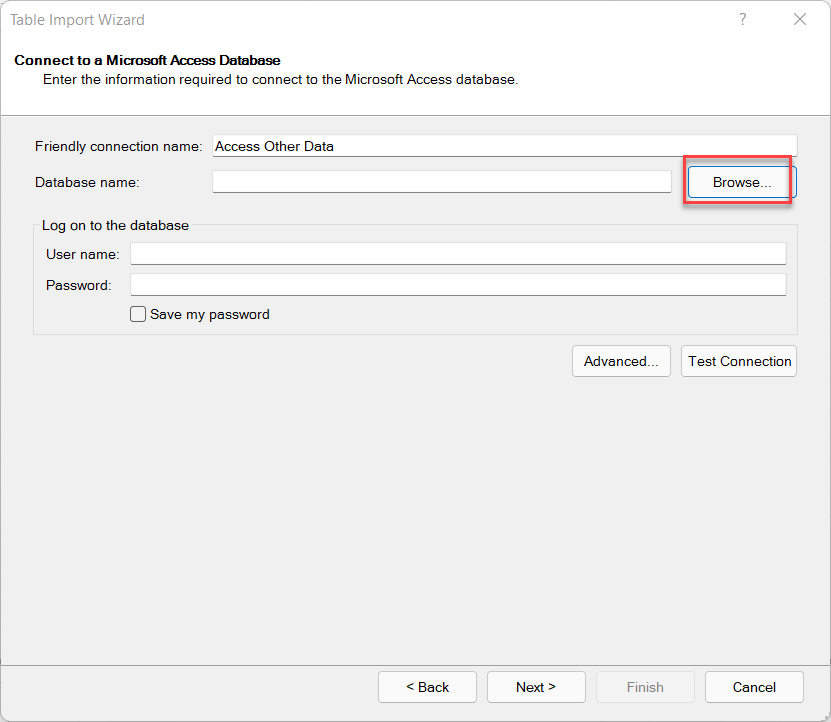
For larger, structured data sources, Power Pivot allows importing data directly from Access databases. This is useful when working with relational data in a corporate environment.
Procedure:
Real-world Application
In a manufacturing company, data on parts, vendors, and production schedules might reside in an Access database. Importing this data into Power Pivot allows linking these tables, enabling inventory analysis, supplier performance evaluation, and production forecasting.
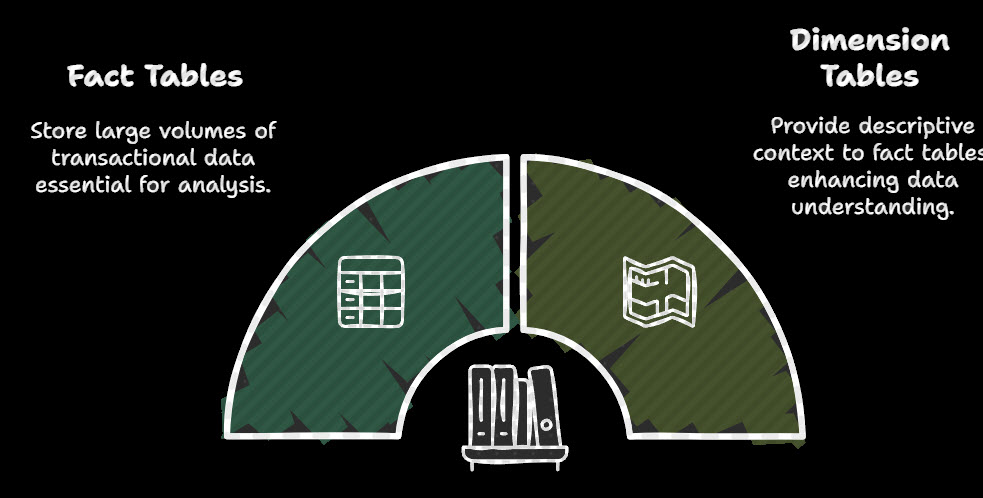
A Data Model in Power Pivot represents a collection of linked tables, creating a structured environment for data analysis. Building an effective data model involves defining fact and dimension tables, calculated columns, and measures. A Star Schema is a common design choice, with a central fact table (e.g., sales transactions) connected to surrounding dimension tables (e.g., customer, date, product).
Key Components of a Data Model
Relationships are vital in Power Pivot, connecting tables to enable cross-referencing and in-depth analysis. By linking tables, Power Pivot allows you to calculate and view data from multiple perspectives.
To build relationships:
Use Case Example
In a healthcare dataset, relationships between Patient, Treatment, and Location tables allow tracking treatments by region, identifying common ailments, and assessing facility utilization. This insight guides strategic decisions in resource allocation.
Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) is a specialized language for creating advanced calculations in Power Pivot. DAX formulas can be used to create calculated columns or measures, adding a layer of sophistication to your analysis. DAX includes functions for time intelligence, making it ideal for businesses analyzing year-over-year or quarter-over-quarter data.
Example of DAX Formula for Profit Calculation:
= ROUND(fct_SalesTransaction[Units Sold] * fct_SalesTransaction[Unit Price], 0)
DAX enables custom metrics that adapt dynamically to the data filters applied, supporting a responsive analytical environment.
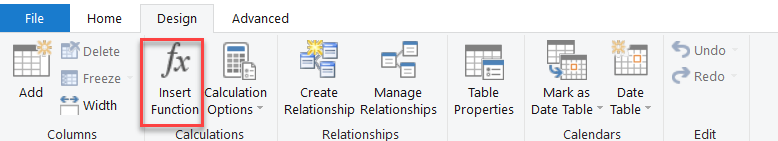
Go to Design > Insert Function to see the list of DAX functions.
Calculated columns are row-level calculations that populate a new column based on a formula. They are ideal for creating metrics like Total Cost or Profit.
Example:
These calculations allow more granular insights, adding value to the data model.
Measures aggregate data across a dataset and are context-sensitive, adapting to filters set in a PivotTable. For example, a measure for Total Revenue would sum values dynamically based on data slicers and filters.
Formula:
Total Revenue M := SUM(fct_SalesTransaction[Total Revenue])
Measures make Power Pivot especially powerful, as they enable dynamic, reusable metrics that adapt to the user’s analysis needs.
Go to PowerPivot > Measures > New Measures.
Table Name = fct_SalesTransaction (This is where measures will be saved).
Measure Name = Conditional Revenue
Formula = Below formula will provide total revenue after going through three filters, such as where Country = “China,” Item Type = “Beverages,” and Sales Channel = “Online.”
Syntax
=
CALCULATE (
SUM ([Total Revenue]),
dim_Location[Country] = “China”,
dim_ItemType[Item Type] = “Beverages”,
dim_SalesChannel[Sales Channel] = “Online”
)
Power Pivot supports creating reports that span multiple tables, making it easy to analyze trends, compare performance metrics, or explore detailed insights.
To create a PivotTable:
Power Pivot supports complex, multi-table data models, allowing advanced calculations and in-depth analyses compared to standard PivotTables, which are limited to single tables.
Power Pivot is embedded in Excel 2016 and later, while it requires a separate download for earlier versions like Excel 2010 and 2013.
A Star Schema is a Data Model design in which a central fact table is surrounded by related dimension tables, improving data query efficiency and clarity.
While similar, DAX functions are specifically designed for data modeling, providing more dynamic and advanced calculations.
A Power Pivot Data Model allows you to combine data from multiple sources, create relationships between tables, and perform advanced calculations. It’s an essential tool for analyzing large datasets efficiently in Excel.
To open the Power Pivot Window in Excel, go to the “Data” tab and click on “Manage” under the Power Pivot section. This window lets you work with data models, create relationships, and add advanced calculations.
Excel Power Pivot enables users to handle large datasets, create complex calculations, and build data models. It simplifies data analysis and helps generate insights with ease, even from diverse data sources.
Mastering Power Pivot opens new possibilities in data analytics, transforming Excel from a spreadsheet tool to an advanced data analysis platform. This comprehensive guide equips you with the fundamentals to harness Power Pivot, build Data Models, and develop meaningful insights from vast datasets. With Power Pivot, Excel’s data-handling capabilities are limitless.

92% of students automate workflows, build CEO-ready dashboards, and streamline collaboration in < 1 hour. Don’t miss out!
🎯Master every Office 365 tool like Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Teams, Outlook and OneNote.
🎯Streamlined approach—no fluff, just rapid skill-building.
🎯Eliminate tedious tasks with intelligent automation.
🎯Transform everyday workflows into strategic power moves.
🎯Boost productivity and impress every boss.
🎯Real-World Projects – directly translate lessons into workplace wins.